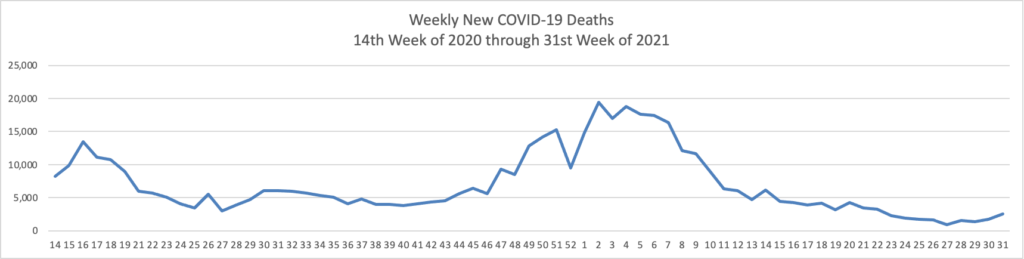
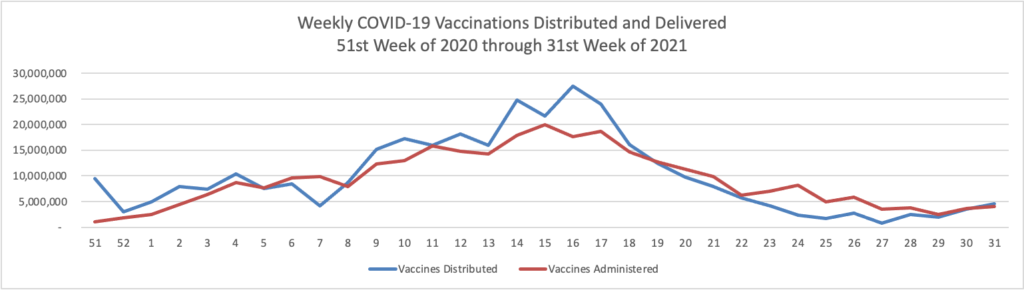
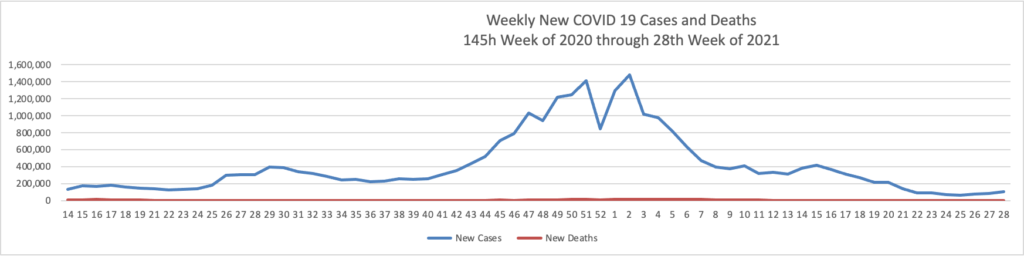
Thursday Miscellany

Govexec reports that
The Veterans Affairs Department will more than triple the number of employees who must receive the vaccine, bringing the total to 360,000. VA originally required just its frontline health care staff—those hired under Title 38 of the U.S. Code—to be inoculated, which amounted to about 115,000 workers.
The mandate will now include Title Five employees within the Veterans Health Administration—such as housekeepers, engineers and administrative staff—and health care providers such as psychologists, pharmacists, physical therapists, nursing assistants and others in “Hybrid Title 38” positions.
“We’re now including most VHA employees and volunteers and contractors in the vaccine mandate because it remains the best way to keep veterans safe, especially as the Delta variant spreads across the country,” Secretary Denis McDonough said. “This pandemic is not over and VA must do everything in our power to protect veterans from COVID-19. With this expanded mandate, we can once again make—and keep—that fundamental promise.”
Employees impacted by the new mandate will have eight weeks to get the vaccine or prove they already have.
In the same vein, the Department of Health and Human Services (“HHS”) announced today that
[HHS] will require more than 25,000 members of its health care workforce to be vaccinated against COVID-19.
Staff at the Indian Health Service (IHS) and National Institutes of Health (NIH) who serve in federally-operated health care and clinical research facilities and interact with, or have the potential to come into contact with, patients will be required to receive the COVID-19 vaccine. This includes employees, contractors, trainees, and volunteers whose duties put them in contact or potential contact with patients at an HHS medical or clinical research facility.
Additionally, U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy will immediately require members of the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps to be vaccinated against COVID-19 as part of medical readiness procedures to prepare for any potential deployment need as emergency responders
Those two mandates apply to about 20% of the federal workforce. In contrast, the general approach is a vaccine screening requirement — either attest to receiving the vaccine or wear a facemask and receive regular COVID-19 testing.
Furthermore, the Wall Street Journal reports that
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorized booster shots for certain people with weakened immune systems, likely the launch of broader efforts to better protect against evasive variants like Delta.
The agency on Thursday cleared giving a third dose of a messenger RNA Covid-19 vaccine from Pfizer Inc. PFE 2.01% and its partner BioNTech SE BNTX 4.13% or from Moderna Inc. MRNA 1.58% to immunocompromised people who had received a solid organ transplant or individuals who have been diagnosed with conditions that are considered to have an equivalent level of immunocompromise.
From the health equity front, the National Institutes of Health released a disturbing study on maternal mortality:
Racial and ethnic disparities in maternal mortality — deaths related to pregnancy or childbirth — in the United States may be larger than previously reported, suggests a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. By re-examining information on death certificates from 2016 and 2017, researchers found that the maternal mortality rate among non-Hispanic Black women was 3.5 times higher than among non-Hispanic white women. Previously, standard analyses had indicated a 2.5-times-higher death rate for Black women.
The new analysis also revealed that these disparities were concentrated among a few causes of death. Postpartum cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle) and the blood pressure disorders preeclampsia and eclampsia were leading causes of maternal death for Black women, with mortality rates five times higher than those for white women. Pregnant and postpartum Black women were two to three times more likely than white women to die of hemorrhage (severe bleeding) or embolisms (blood vessel blockages).
The study was funded by NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and led by Marian MacDorman, Ph.D., of the Maryland Population Research Center at the University of Maryland. It appears in the American Journal of Public Health.
Healthcare Dive reports on HIMSS conference presentations on this important topic of achieving health equity.
Healthcare executives do say equity is a top priority for their organizations, with half of the CEOs surveyed by Deliotte early this year saying its among their top three organizational priorities this year, according to a recent report from the consultancy.
However, companies are at different stages of actually implementing equity and inclusion programs, with some reporting they’ve been focused on addressing disparities for years, and others just beginning to define what it means to their organization.
Of the 20 chief executives surveyed by Deliotte, 17 said they had a dedicated team or budget for health equity initiatives.
That top-level buy-in is important, but addressing health inequities needs to be a whole-enterprise mission, [Ronald] Copeland[, the chief equity, inclusion and diversity officer for integrated health giant Kaiser Permanente] said, integrated into every facet of payer and provider goals. One strategy to achieve this could be to make health equity a formal dimension of quality improvement, a policy that’s even recently been considered in federal payer programs under the Biden administration.
In other HIMSS conference news —
- Fierce Healthcare informs about HIMSS conference discussion on rationalizing patient and provider experiences with multiple front end apps.
- Healthcare Dive interviews Teladoc’s president of hospitals and health systems, Joe DeVivo about the state of the telehealth market and the company’s ambitions.
STAT News informed us today that 19,000 people attended the HIMSS conference in person and 5,000 attended virtually. 700 exhibitors attended. Both of those totals are about half of the normal in person attendance at HIMSS.
From the drug costs front, the White House released the President’s ideas on how to reduce prescription drug costs. The President leads off with encouraging Congress to allow CMS to negotiate Medicare Part D drug contracts. That change may save money for the federal government but it shift those savings to the commercial sector including the FEHB.
Also the HHS Inspector General released a report on opioid use among Medicare beneficiaries in 2020. “More than 43,000 Medicare Part D beneficiaries suffered an opioid overdose—from prescription opioids, illicit opioids, or both—in 2020.” The Inspector General also noticed a drop in prescriptions for opioid treatments which the OIG found concerning. “A May 2020 OIG data brief recommended that CMS educate Part D beneficiaries and providers about access to MAT drugs and naloxone. We continue to encourage CMS to take these steps. It is also critical for CMS to closely monitor the number of beneficiaries receiving MAT drugs and naloxone and take action, if needed. OIG is also committed to continuing our work on opioid use and access to treatment.”
In litigation news, the prescription benefit manager trade association, PCMA, has filed a lawsuit against HHS in the District of Columbia’s federal court challenging the legality of certain aspects of the payer transparency rule scheduled to start phasing in on January 1, 2022.
PCMA is not challenging the portions of the rule that direct plans to provide useful information directly to patients. But we are challenging the portions of the rule that do not meet those important objectives and will not produce information that patients and physicians can use.
These parts of the Trump administration’s transparency rule will drive prescription drug costs higher. By requiring disclosure of “historical” net prices, which are essentially current year net prescription drug prices, the rule will directly provide drug manufacturers access to their competitors’ negotiated rebates, discounts, and price concessions. This in turn will allow drug manufacturers to discount less deeply as they realize their price concessions went beyond those of competitors.
In addition, outside entities will not be able to develop reported information into a useful and understandable format for patients. Unlike health plans and PBMs, third-party application developers will not know patients’ existing insurance enrollment and eligibility or their current benefits and whether they have met a deductible or reached an out-of-pocket limit, and so the third-party applications are likely to cause widespread confusion among patients. Net prices are generally not useful information to patients because their deductible and coinsurance payments are calculated based on negotiated rates, not net prices.
PBMs and health plans already have real-time benefits tools for patients and prescribers, which they can use at the point of prescribing to check on cost-sharing for every patient based on their individual situation and health plan.
Coincidentally, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce has filed a substantially similar lawsuit in the federal court for the Eastern District of Texas. That case challenges the legality of the “historical net prices” provision and the “three machine readable tapes” provision of the HHS rule on the ground that they have no utility to consumers. Good luck.
Finally, the Census Bureau released a lot more 2020 census data today. The Wall Street Journal observes that “The nation’s population grew just 7.4% during the decade, the second slowest on record for a decennial census. Only the 1930s—the era of the Great Depression—saw slower growth.”