Thursday Miscellany

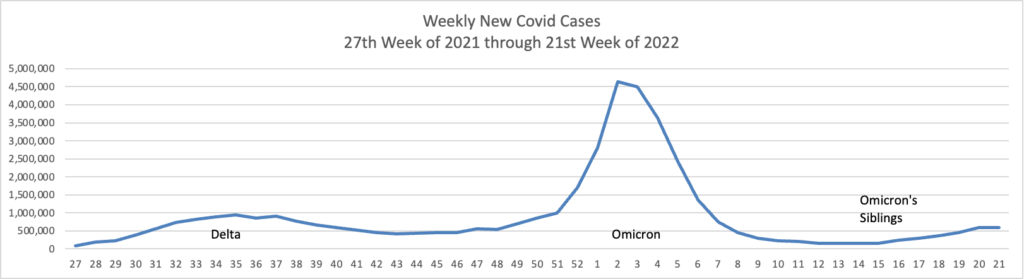
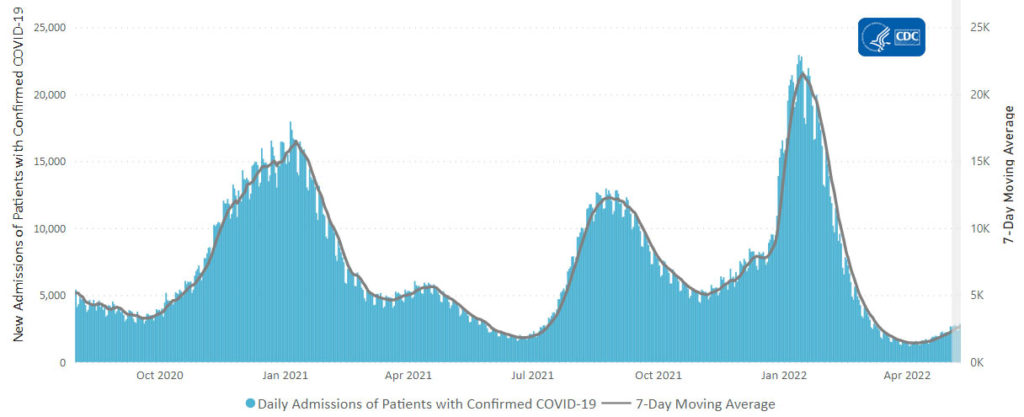
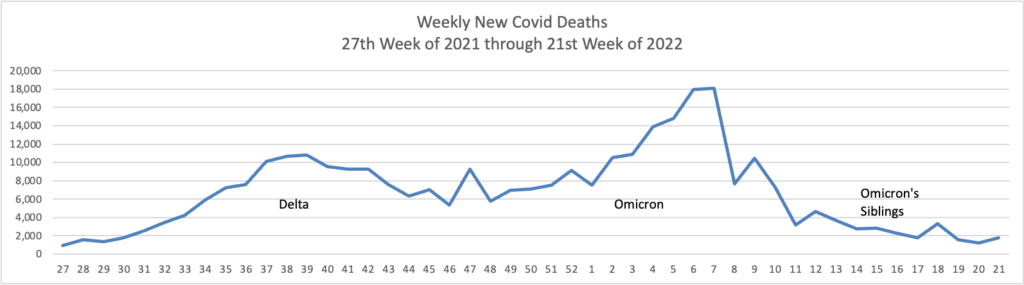
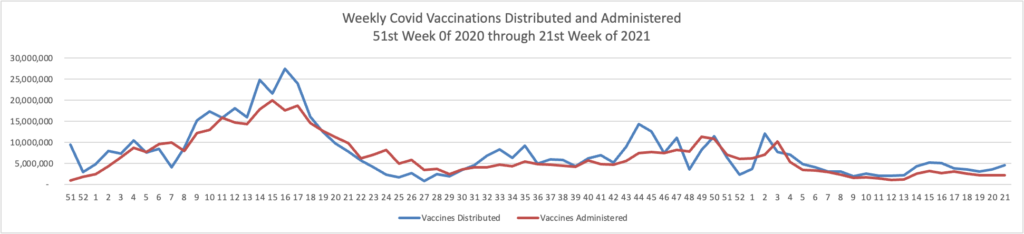
From the Omicron and siblings’ front —
MedPage Today reports “Second COVID booster shot boosted antibodies in Seniors — but small Israeli study did not determine how quickly response will wane.”
Becker’s Hospital Reviews tells us
At least 18 cases of the newest omicron subvariant BA.2.75 have been confirmed in seven U.S. states as of July 20, early disease surveillance data shows.
Globally, researchers have identified 201 cases in more than a dozen countries as of July 12, according to data from outbreak.info, a platform that tracks data on coronavirus variants and is supported by the CDC and other national research groups.
The subvariant has a large number of mutations that may make it more adept than BA.5 — the nation’s current dominant strain — at spreading quickly and evading immune protection. Experts say it’s still unclear whether BA.2.75 will compete against BA.5 or cause more severe illness, according to CNN.
This leads us to the Wall Street Journal’s editorial board comments
The President’s [Omicron] infection [disclosed today] demonstrates how hard it is to avoid the new and highly transmissible Covid variants. The White House has gone to great lengths to protect Mr. Biden, but there’s only so much staff can do if the President is going to do his job.
Despite continuing pleas from the White House and public-health elite, vaccination by now provides little protection against transmission. * * * The evidence is that the vaccines do reduce the chances of getting serious Covid and being hospitalized, though many elderly patients who have been vaccinated are still dying from the virus.
While this quote is an opinion, not a news report, it struck a chord with the FEHBlog. The FEHBlog wishes the President a speedy recovery.
From the unusual viruses front, the Department of Health and Human Services offers a fact sheet on its response to the monkeypox outbreak.
In mergers and acquisitions news, Healthcare Dive informs us
Amazon has agreed to acquire primary care network One Medical for $18 a share, valuing the company at $3.9 billion.
The all-cash deal for San Francisco-based One Medical comes after months of speculation about a potential acquisition, reportedly drawing interest from companies including CVS Health, according to Bloomberg.
Analysts said a potential buyout for One Medical, which has grown rapidly since it was founded in 2007, could come at a significant premium. Amazon’s price of $18 a share represents a premium of 43% over its closing price of $10.18 a share on Wednesday.
STAT News explains why Amazon pursued adding One Medical to its healthcare portfolio.
With One Medical, Amazon is also tapping deeper into the vein of health care’s payment system. One Medical gets paid through two main avenues: commercial health insurers and Medicare. The Medicare side came from Iora, which One Medical bought for $1.4 billion last year.
Commercially insured patients, or those who get coverage through their jobs, are by far the most profitable within health care and overlap with a large chunk of Amazon’s subscription base. Even though One Medical focuses on less expensive primary care, there’s evidence One Medical charges some of the highest rates for those routine office visits and services, and that’s largely assisted by One Medical’s hospital partners.
Hospitals pay fixed sums to One Medical to care for patients, but they also “extend their health insurance contracts” to One Medical, the company said when it went public in 2020. The result: Hospitals that ink deals with One Medical get the most profitable patients in their market referred to them for more intensive services, and One Medical gets to piggyback off the lucrative payments that those dominant hospitals wring out of insurers.
STAT News concludes
Amazon’s success — and how disruptive it might prove to be to telehealth competitors — will depend in part on how well it integrates One Medical into its existing in-person and virtual offerings through Amazon Care. Analysts said that will become clear over the next year.
Whether it does draw patients away from traditional health care providers depends on their partnership with payers and their fees, said Aaron Neinstein, vice president of digital health for UCSF Health. “There’s no question that the One Medical annual fee is out of reach for most people in the U.S. Might Amazon change that or bundle it with Prime? Who knows.”F
Health Leaders Media reports that, notwithstanding the Federal Trade Commission’s nascent efforts,
Hospital and health system mergers and acquisitions in Q2 of 2022 have returned to trendlines that Kaufman Hall has been following since the beginning of the pandemic, the consulting firm said in its recently released M&A quarterly report.
During the second quarter of 2022, there were 13 hospital and health system M&A transactions, on-trend and only one transaction less than the 14 transactions reached in Q2 of 2021 and 2020. However, the total transacted revenue in the second quarter reached a “historic high” of $19.2 billion, more than doubling the $8.5 billion transacted revenue in the same quarter in 2021.
From the reports department and via Axios, the FEHBlog ran across this comprehensive McKinsey and Company report on the future of U.S. healthcare: what’s next for the industry post-Covid. Check it out.
From the Rx coverage front, DrugChannels calls our attention to this Amgen preview of 2022 trends in the biosimilars market. Adam Fein observes
As I predicted two years ago, the biosimilar boom is finally here. Prices are dropping while adoption accelerates. Prices are now declining by 9% to 22% annually. For therapeutic areas with biosimilars launched in the last three years, biosimilars’ market share averages 74%. See Amgen slides 8 and 9.
Before the boom began, Dr. Scott Gottlieb, a former FDA commissioner, argued that we shouldn’t give up on biosimilars and prematurely regulate prices. As we can now see, Dr. Gottlieb was right. #NoTowel
From the SDOH front, Health Payer Intelligence explains
Race and ethnicity data collection is complex, but there are steps that health insurers—and the healthcare industry at large—can take to improve the process, according to a report from Urban Institute funded by Elevance Health (formerly Anthem).
From the miscellany department
- Fierce Healthcare discusses a recent Fitch report on non-profit hospitals.
Labor, supply and capital cost increases have been rampant across the industry this year thanks to broader inflation pressures and other pandemic factors, the ratings agency wrote.
Reversing the margin trends will likely require nonprofit hospitals to take on a combination of rate hikes in the short term, “relentless” cost-cutting and productivity initiatives for the medium term and “transformational changes to the business model” for the long term, Fitch wrote.
Fortunately for those hospitals, many organizations already have the means to weather the storm as they overhaul their operations.
“The vast majority of our rated credits have strong balance sheets that will offset lower margins for a period of time and allow for operational improvements,” Fitch wrote. “Without more substantial changes to the current business model, or with additional coronavirus surges this fall or winter, this balance sheet cushion could eventually erode.”
Rate negotiations with payers will likely be an upward battle, the group wrote.
- Healthcare Forefront points out the value of underutilized fentanyl test strips
Fentanyl test strips (FTS) are a simple, inexpensive, and evidence-based method of averting drug overdose. FTS are small strips of paper that can detect the presence of fentanyl in any drug batch—pills, powder, or injectables. This tool might be lifesaving for the teenager experimenting for the first time, the individual in the throes of a severe opioid use disorder, the concert-goer looking for a trip, the person using a preferred substance obtained from a new source, or the individual years into recovery. FTS also support the dignity and well-being of people who use drugs (PWUD), enabling them to make educated decisions about their safety.
And yet after years of press and discussions of the strips’ utility, FTS aren’t as widely available as one would expect them to be. It is time to take a more critical look at the importance of destigmatizing this tool and increasing its distribution and availability, while highlighting the grave risks in not doing so.
- HealthDay gives us some good news.
U.S. hospitals became much safer places for patients over the past decade, with medical errors and adverse events declining significantly across the nation, federal government data show.
Between 2010 and 2019, patient safety dramatically improved among the four types of conditions for which people are most often hospitalized: heart attacks, heart failure, pneumonia and major surgical procedures.
“There has been a precipitous, very important drop in the number of these events, which to me validates the idea that these were preventable,” said senior researcher Dr. Harlan Krumholz, director of the Yale New Haven Hospital Center for Outcomes Research and Education in New Haven, Conn. “The status quo wasn’t written in stone. We have been able to actually make hospitals safer for those conditions.”
The new study relied on data gathered by the Medicare Patient Safety Monitoring Program, an effort created in the wake of a landmark 1999 Institute of Medicine report that drew national attention to patient safety in hospitals, the study authors said in background notes.
- Fedweek reviews the steps that federal employees should take to position themselves for retirement.