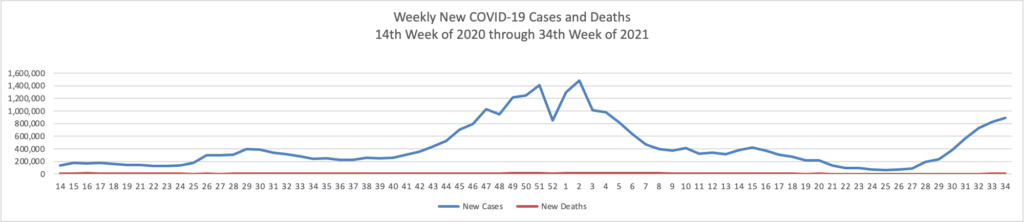
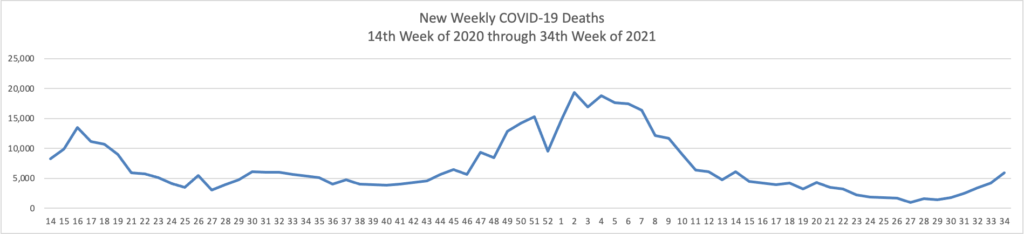
Tuesday Tidbits

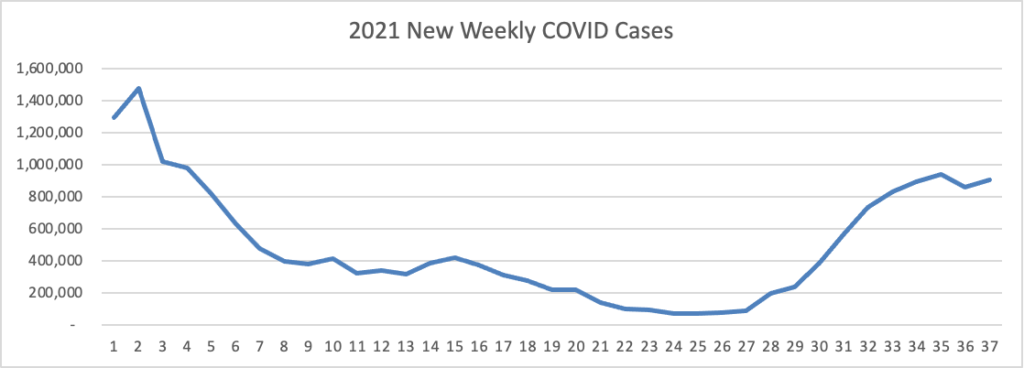
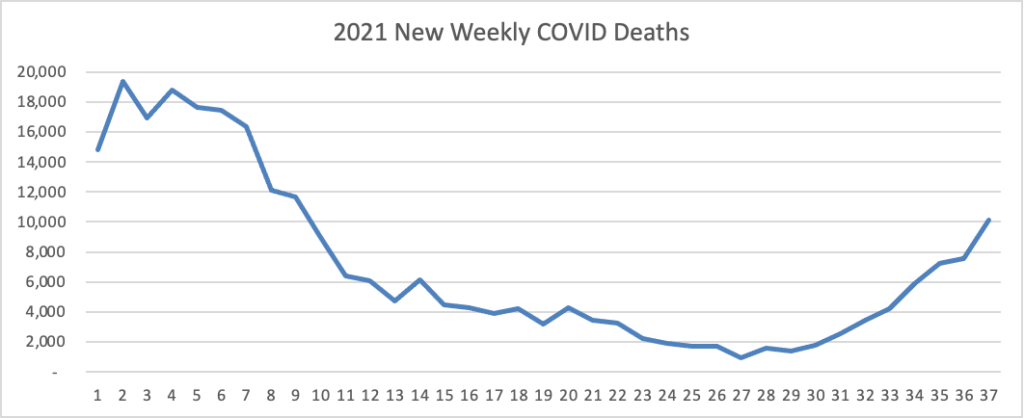
From the Delta variant front
- The New York Time reports that “Johnson & Johnson on Tuesday morning asked federal regulators to authorize a booster shot for adults, becoming the third coronavirus vaccine manufacturer to do so.”
- Fierce Healthcare tells us that
AstraZeneca has taken another step toward bringing its COVID-19 antibody cocktail to market, filing for emergency use authorization of the long-acting candidate in coronavirus prophylaxis in the U.S.
Last month, AstraZeneca delivered evidence that the candidate prevents COVID-19 in people who are unlikely to respond well to vaccines, bouncing back from an earlier failure to report a 77% reduction in the risk of symptomatic coronavirus infection. With all three cases of severe COVID-19 happening in the placebo cohort, AstraZeneca emerged from the study with evidence that it can protect some of the most vulnerable people from the coronavirus.
“Vulnerable populations such as the immunocompromised often aren’t able to mount a protective response following vaccination and continue to be at risk of developing COVID-19. With this first global regulatory filing, we are one step closer to providing an additional option to help protect against COVID-19 alongside vaccines,” Mene Pangalos, executive vice president for biopharmaceuticals R&D at AstraZeneca, said in a statement.
In his final National Institutes of Health Director’s blog today. Dr. Francis Collins optimistically supports his opinion that most COVID vaccine hesitant people are willing to change their minds. “Over the course of this pandemic, hesitancy has decreased, and many who initially said no are now getting their shots. Many others who remain unvaccinated lean toward making an appointment. The findings come from Aaron Siegler and colleagues, Emory University, Atlanta.”
Dr. Collins today submitted his resignation from his position as NIH Director following over 12 years in that role. His statement reads in part “It has been an incredible privilege to lead this great agency for more than a decade,” said Dr. Collins. “I love this agency and its people so deeply that the decision to step down was a difficult one, done in close counsel with my wife, Diane Baker, and my family. I am proud of all we’ve accomplished. I fundamentally believe, however, that no single person should serve in the position too long, and that it’s time to bring in a new scientist to lead the NIH into the future. I’m most grateful and proud of the NIH staff and the scientific community, whose extraordinary commitment to lifesaving research delivers hope to the American people and the world every day.” Good luck, Dr. Collins, who will continue working in his genetics laboratory.
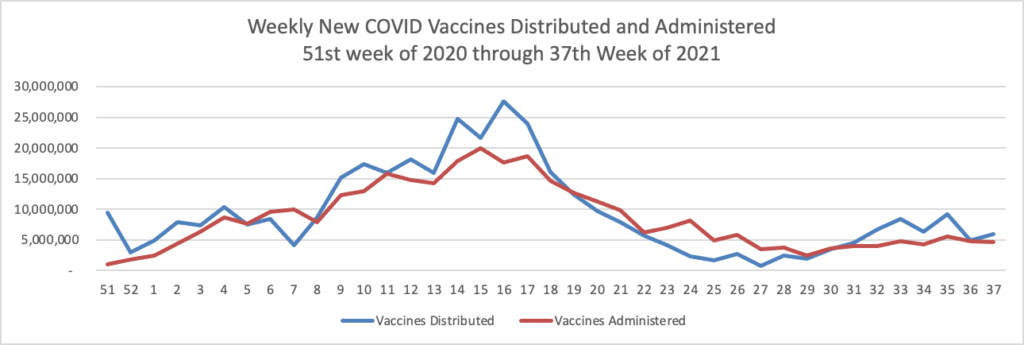
From the COVID vaccine mandate front, the Safer Federal Workforce Taskforce released more FAQs on the vaccine mandate for federal employees yesterday. Federal News Network summarizes those FAQs here:
Employees have a few more details about what they should expect if they’re planning to declare a medical or religious exception to the Biden administration’s recent federal vaccine mandate.
Employees who have previously had COVID-19 must receive the vaccine, the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force clarified Monday night in another round of frequently asked questions. The task force had previously made such a statement in guidance to contractors, not federal employees.
The Biden administration didn’t detail exactly what kinds of medical or religious reasons might grant an employee an exception to the federal vaccine mandate, but it did offer more hints about what employees might expect if they pursue that route.
More significantly in the FEHBlog’s view, Federal News Network reports that the Defense Department has “issued its guidance for civilian employees on Monday, giving workers [until November 22] to get inoculated.” In order to achieve this goal an employee must have received the Johnson & Johnson one dose vaccine or both doses of the Pfizer or Moderna by November 8 because the full vaccination status accrues two weeks are being fully vaccinated.
From the mergers and acquisitions front, Becker’s Hospital Review tells us that “More than three years after signing a letter of intent to merge [and overcoming regulatory challenges], Jefferson Health and Einstein Healthcare Network have finalized the deal. The combination of the Philadelphia-based organizations brings together two academic medical centers and creates an integrated 18-hospital system with more than 50 outpatient and urgent care locations.”
From the tidbits department:
- Healthcare Dive informs us that
Allowed in-network charges for fixed-wing air ambulances rose 76% between 2017 and 2020, and now top $15,000, a new study by Fair Health found. The average charge rose 27.6% during the same time period, to more than $24,500 from little more than $19,200. For helicopter transports, the average allowed charge rose 60.8%, from just over $11,600 to more than $18,600.
Meanwhile, the average Medicare reimbursement rose much less dramatically between 2017 and last year, and represents just a fraction of what commercial insurers are charged for air ambulance transports.
Demand may be part of the equation. Fair concluded that air ambulance claims rose 30% between 2016 and 2020. The leading reasons for such transports are digestive issues, heart attacks and bone breaks or fractures. The states with the largest volumes of fixed-wing air transports are rural: Alaska, Wyoming, South Dakota, Montana and New Mexico. For helicopters, it’s Idaho, South Dakota, New Mexico, West Virginia and Wyoming.
- Health Payer Intelligences delved into the American Medical Association’s annual report on health insurer competition. Kaiser Permanente joined UnitedHealthcare, Anthem, Aetna, and Cigna in the top five.
- Health Payer Intelligence also tells us that
A new study finds that while telehealth has surged during the pandemic, providers haven’t solved many of the issues that kept adoption low prior to COVID-19.
J.D. Power’s 2021 US Telehealth Satisfaction Survey, released this week, saw a surge in telehealth use from 7 percent in 2019 and 9 percent in 2020 to 36 percent in 2021, reflecting the shift to virtual care as the nation grappled with COVID-19. But the consumer advisory company’s third annual survey also saw a decrease in patient satisfaction, driven by complains over limited services (24 percent), lack of awareness on costs, confusing technology requirements and lack of information about care providers (all at 15 percent).
The more things change, etc.
- STAT News reports that
It’s one of the biggest market failures in modern medicine. The lack of a widely shared data language is effectively blocking adoption of innumerable software applications designed to make health care cheaper, more effective, and personal.
On Tuesday, three large health systems formed a new nonprofit company to fill that gap. The venture, dubbed Graphite Health, is seeking to build an App-Store-like marketplace where digital health entrepreneurs can sell their software tools, and hospitals and consumers can more easily buy and implement them.
Its founders, including Intermountain Healthcare of Utah, previously launched CivicaRX, another hospital-led nonprofit built to create a cheaper, more reliable supply of generic medicines. If it gains the same level of uptake, Graphite could essentially eliminate the long and costly process of vetting and customizing software that hospitals use to do everything from selecting the best treatments for patients to managing their beds and operating rooms. It will also offer a range of apps for patients.