Monday Roundup

From Capitol Hill —
The Federal Times seeks to project the timeline for implementing the new law requiring the Veterans’ Administration to cover illnesses contracted by Iraq and Afghanistan veterans who were exposed to burn pit smoke while overseas.
The Republicans on the House Ways and Means Committee offer their perspective on the budget reconciliation bill that Senate passed yesterday and the House will take up this Friday.
From the OPM front, the FEHBlog noticed today that its Office of Inspector General (OIG) has posted on its revamped website the OIG’s semi-annual report to Congress for the period ended March 31, 2022. This report is always worth a gander to those who are interested in the FEHB Program.
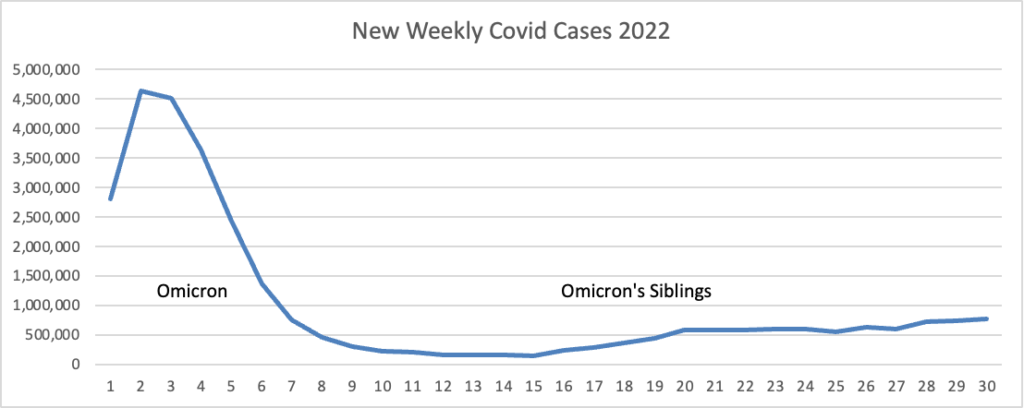
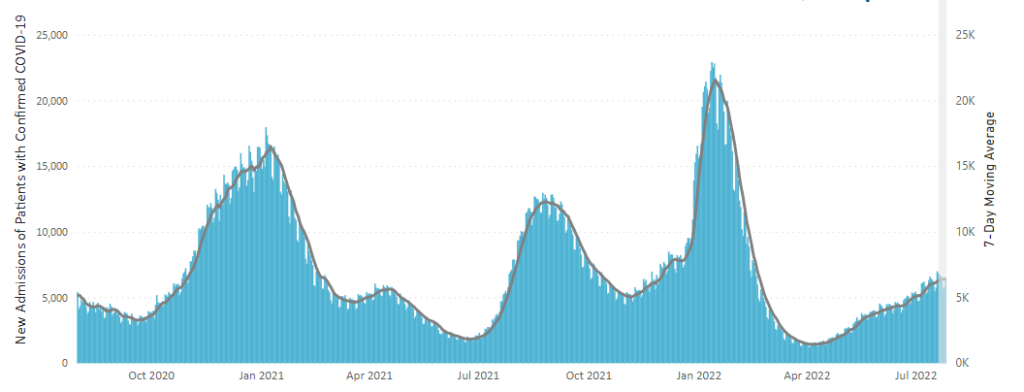
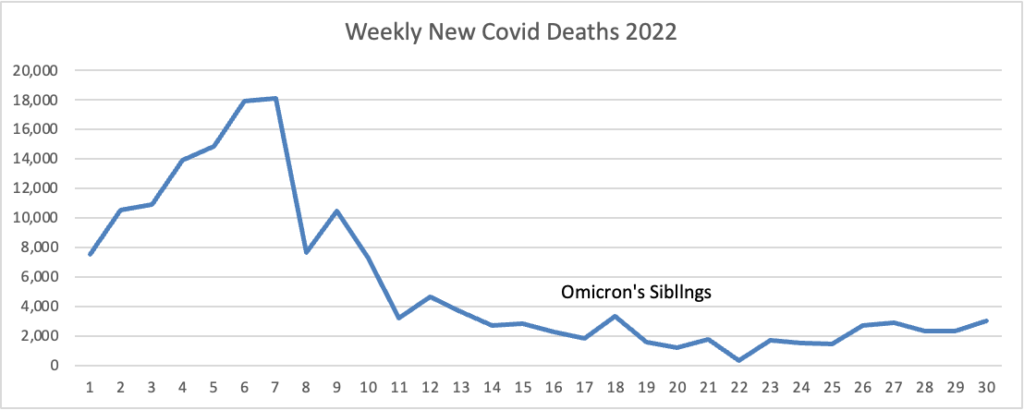
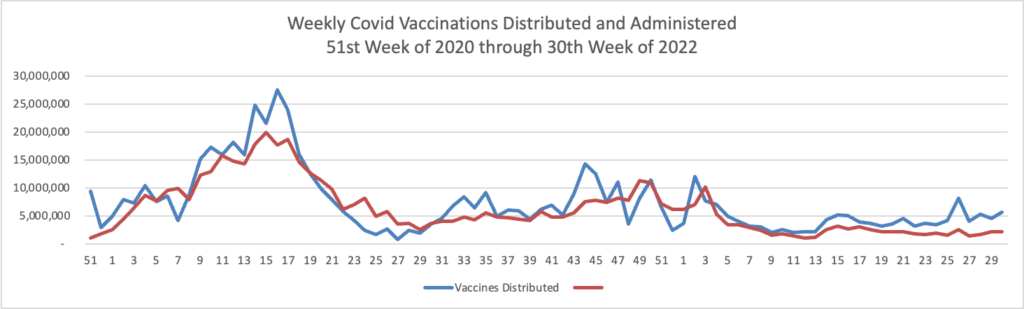
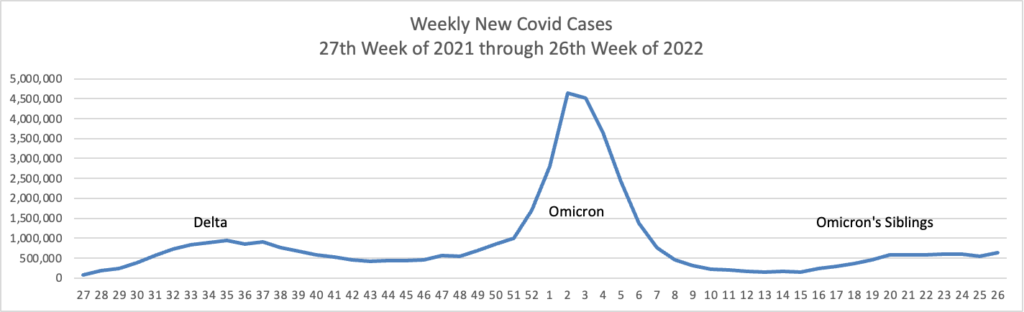
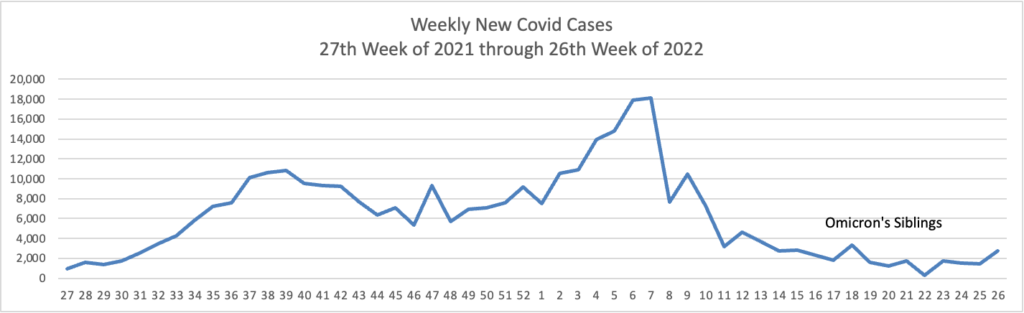
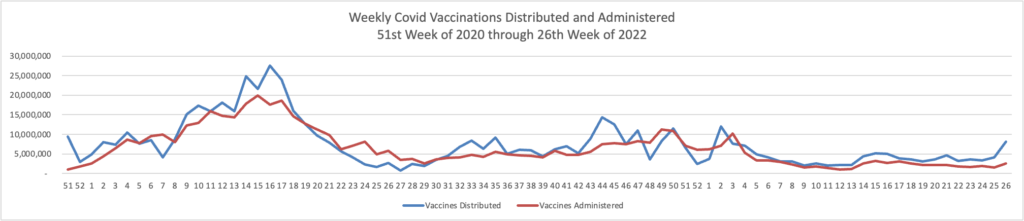
From the Omicron and siblings front, the Wall Street Journal reports
Parents are having their say about the Covid-19 vaccines for children under 5, and for most, the answer so far is no.
More than a month after the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended shots for about 17.4 million children ages 6 months through 4 years, about 4% to 5% of them have received a shot, according to the most recent agency data and population estimates from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
By contrast, the vaccination rate for children 5 to 11 years reached about 18% a month after the CDC first recommended shots last November. The rate now stands at about 38%. * * *
Uptake has varied by state, recent counts from around the U.S. show. In Massachusetts, roughly 40,541 children under 5, about 11% of the state’s population in that age group, have received one dose. In New Jersey, more than 21,000 young children, or 4.6% of the children under 5 in that state, have received one dose.
A lawyer writing on the Society for Human Resource Management advises “employers with workers who test positive for COVID-19 should follow guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), including its guidelines on quarantining and isolation, to minimize safety and legal risks, even though the guidance is somewhat complex.”
From the public health front, the Department of Health and Human Services announced today its Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) is
awarding nearly $90 million in American Rescue Plan funding to nearly 1,400 community health centers across the country to advance health equity through better data collection and reporting. On Friday, August 5, President Biden issued a proclamation on National Health Center Week to recognize the vital role health centers play in safeguarding the well-being of Americans and honor the heroic staff who keep these facilities running.
What’s more, the American Hospital Association tells us
[HRSA] today awarded $45.7 million from the American Rescue Plan Act [ARPA]to develop the public health workforce in rural and tribal communities. The grants will help train dental hygienists, medical and dental assistants, doulas and other community health workers; health information technology and telehealth technical support staff; community paramedical workers; and respiratory therapists and care coordinators for patients with long-term COVID-19 effects and chronic medical conditions.
In addition to the ARPA grants, the agency awarded $9.7 million to help hospitals and others establish new medical residency programs in rural communities; $2.9 million to improve health outcomes in rural counties; and nearly $1 million to improve access to care for rural veterans.
From the No Surprises Act front, Healthcare Dive informs us
The Medical Group Management Association, which represents physician practices, is urging the HHS and the CMS to delay enforcing certain requirements of the No Surprises Act to allow providers time to understand and implement the mandates.
In a letter to HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra and CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks La-Sure, MGMA asked that medical group practices be given six months’ notice before enforcement of additional surprise billing requirements.
The provider group requested the enforcement delay following publication of more anticipated rulemaking including an advanced explanation of benefits, continuity of care protections and provider directory requirements.
The FEHBlog supports the MGMA’s position because Congress goofed in the NSA by not treating the good faith estimate and advance EOB as HIPAA electronic transaction standards.
STAT News discusses the stress that providers and payers are experiencing as they wait for the Labor Department to issue its final rule (following receipt of public comments on its interim final rule) about the NSA’s independent dispute resolution process.
From the Rx coverage front, STAT News reports
Karuna Therapeutics said Monday that a novel combination pill reduced psychosis and related symptoms experienced by patients with schizophrenia, achieving the main goals of a late-stage clinical trial.
With positive study results in hand, the Boston-based biotech intends to submit a marketing application with the Food and Drug Administration by the middle of next year. If approved, the Karuna drug would usher in the first new class of medicines for the treatment of schizophrenia in decades.
Called KarXT, the Karuna drug targets muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain to reduce psychotic symptoms. Current antipsychotics — which mostly block dopamine receptors — have become blockbuster schizophrenia medicines despite causing troubling side effects like weight gain and somnolence. Peak sales for KarXT could also reach into the billions of dollars, analysts forecast.
That’s certainly encouraging.
From the U.S. healthcare business front —
Fierce Healthcare reports
Kaiser Permanente posted a thinned operating margin and nearly $1.3 billion net loss during its second quarter “driven largely by investment market conditions,” according to topline financials for the quarter ended June 30 reported Friday evening.
The massive integrated nonprofit health system notched $23.47 billion in total operating revenues, representing a minor 0.9% dip from the second quarter of last year. Total operating expenses inched nearly 0.2% upward year over year, to $23.38 billion.
The result was an operating income of $89 million (0.4% operating margin) during the most recent quarter, down from the prior year’s $349 million (1.5% operating margin).
“Much like the entire health care industry, we continue to address deferred care while navigating COVID-19 surges and associated expenses. Kaiser Permanente’s integrated model of providing both care and coverage enables us to meet these challenges as demonstrated by our moderate increase in year-over-year operating expenses for the second quarter,” EVP and Chief Financial Officer Kathy Lancaster said in a statement accompanying the filing.
BioPharma Dive informs us
Pfizer on Monday said it has agreed to acquire Global Blood Therapeutics for $5.4 billion in a deal that will hand it a recently approved drug for sickle cell disease, as well as two other experimental medicines for the rare blood condition. Under terms of the deal, Pfizer will pay $68.50 in cash per Global Blood share * * *. * * * Pfizer and Global Blood expect the deal, which has been approved by the boards of directors at both companies, to close as early as the fourth quarter, pending the sign off regulators and Global Blood shareholders.
Becker’s Hospital Review is running a series on health information interoperability:
Health data interoperability has long been a goal of health IT executives and policy experts. But it’s 2022 — and the healthcare system doesn’t appear all that close to getting there.
Becker’s spoke to experts from health systems, industry and academia on what it will take to create an open exchange of healthcare information in the U.S.
The first entry in the series is a Q&A with Donna Roach, CIO of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City
Check it out.