Thursday Miscellany

From Capitol Hill, Federal News Network identifies five federal workforce items on Congress’s to-do list.
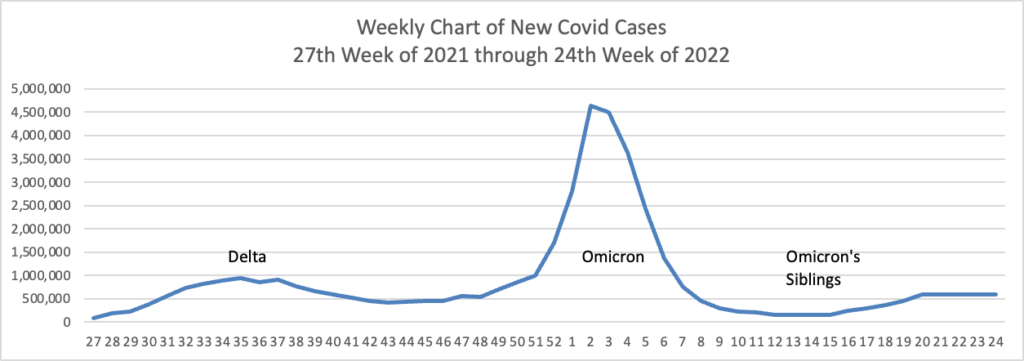
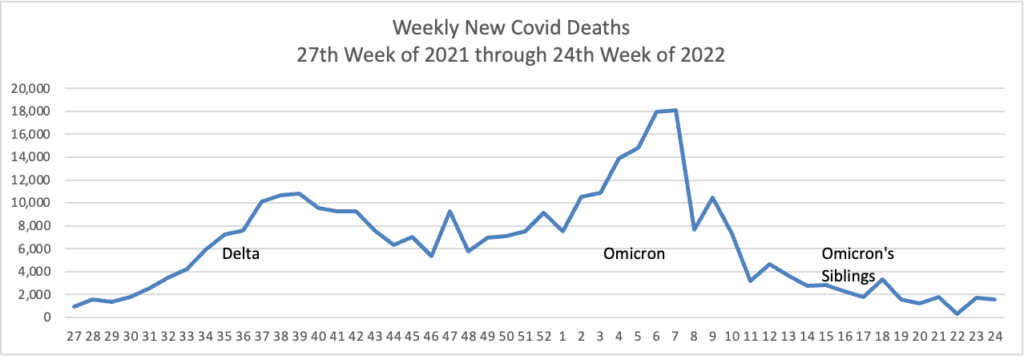
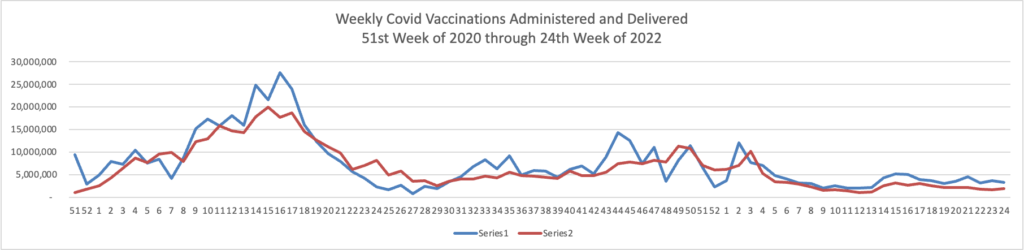
From the omicron and siblings front, the Wall Street Journal reports
The Biden administration is planning for an end to its practice of paying for Covid-19 shots and treatments, shifting more control of pricing and coverage to the healthcare industry in ways that could generate sales for companies—and costs for consumers—for years to come. * * *
Shifting payments for Covid-19 drugs and vaccines to the commercial market is expected to take months, an HHS spokesman said. * * *
Switching vaccine purchasing to the commercial market would mean that each insurer and pharmacy benefit manager would be negotiating with drug manufacturers and prices would likely be higher than what the federal government has paid, said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. Insurers would have to start paying for the vaccines, he said, likely raising premiums.
MedPage Today informs us
More than 2 years after patients started reporting long-lasting symptoms after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, the U.S. announced its national long COVID plan.
The National Research Action Plan on Long COVID aims to improve prevention, diagnosis, and treatment for long COVID, which currently affects up to 23 million people in the U.S., about 1 million of whom may be out of the workforce at any given time because of the condition, according to Admiral Rachel Levine, MD, HHS assistant secretary for health. * * *
Long COVID advocates expressed mixed opinions. Hannah Davis, co-founder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, noted the fact that “there’s going to be an [Office of Long COVID Research and Practice] is pretty amazing.”
But Davis voiced concerns about the scarcity of prevention efforts addressed by the plan. “I think there’s still a feeling like we can get through this without minimizing cases, but we really need to be focused on prevention as well,” she said.
Diana Berrent, founder of Survivor Corps, told MedPage Today that the administration “nailed the institutional challenge of long COVID” but also thought the plan was insufficient.
“Millions of Americans, young and old, are suffering the aftermath of COVID and need immediate relief from their pain,” Berrent said. “An established office in HHS is a welcome step but nothing short of actual treatments and therapeutics will do the trick.”
From the monkeypox front, Becker’s Hospital Review provides a state-by-state breakdown of monkeypox cases, and MedPage Today reports
The Biden administration is making an additional 1.8 million doses of the Jynneos monkeypox vaccine available beginning Monday, and will be targeting certain large events — such as gay pride marches that attract many LGBTQIA participants — as sites for monkeypox vaccination and outreach, administration officials said Thursday.
From the healthcare costs front, Healthcare Dive reports
U.S. employers will pay 6.5% more on average for employee healthcare coverage in 2023 compared to this year, according to an Aon report out Thursday.
The latest predicted rise, while a jump from the 3.7% growth in employer costs between 2021 and 2022, is still far below the 9.1% Consumer Price Index, a figure reflecting inflation.
Inflation typically hits healthcare costs later than other goods and services due to the multi-year nature of contracts between providers and insurers, but impacts will become more prevalent over the year, according to the report.
Speaking of higher costs, Fierce Healthcare discusses Moody’s report on how an economic downturn would impact health plans.
From the post-Dobbs front, the FEHBlog ran across this Congressional Research Service FAQs on Federal Resources for Reproductive Health.
From the No Surprises Act front, the American Hospital Association informs us “The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has launched a new webpage with resources and guidance related to the dispute resolution process under the No Surprises Act, including guidance for disputing parties and a walkthrough of the federal portal. CMS also has added functionality to the portal for initiating disputes, including a button to upload supporting documents at initiation.”
From the miscellany department —
- Fierce Healthcare discusses J.D. Powers’ annual study of Medicare Advantage plans. “[T]he analysts found members’ general satisfaction is up from 2021 and is higher than satisfaction reported by people in employer-sponsored plans. However, while members said they’re happy with access to preventive and routine care, coverage of mental health and substance abuse treatment is lacking.”
- STAT News calls our attention to “a new Pew-funded report, by researchers at George Washington University, the federal government can expand methadone access without approval from Congress.” According to the article, “When it comes to fighting opioid addiction, there’s no tool more effective than methadone. Doctors have been prescribing the drug since the 1960s, and patients who use it are far less likely to experience an overdose.”
- The National Cancer Institute “will award $23 million to four academic institutions to establish centers of excellence that will conduct research on the role of telehealth in delivering cancer-related health care, a practice that became more prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic.“