Thursday Miscellany

The Hill reports
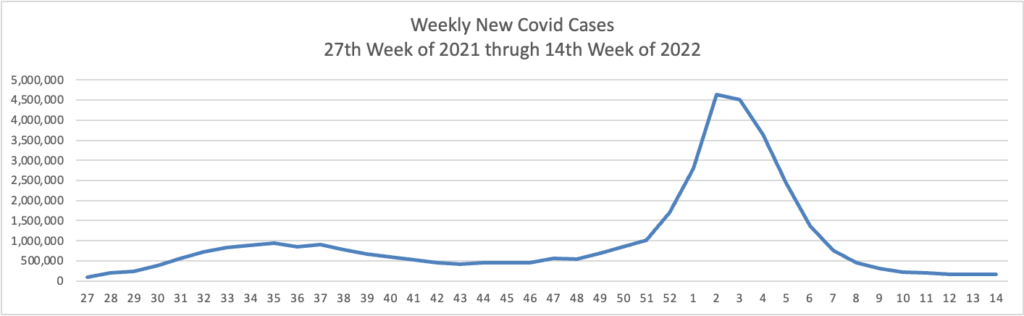
White House COVID-19 coordinator Dr. Ashish Jha issued a dire warning Thursday that the U.S. will be increasingly vulnerable to the coronavirus this fall and winter if Congress doesn’t swiftly approve new funding for more vaccines and treatments.
In an Associated Press interview, Jha said Americans’ immune protection from the virus is waning, the virus is adapting to be more contagious and booster doses for most people will be necessary — with the potential for enhanced protection from a new generation of shots.
STAT News offers this ray of sunshine
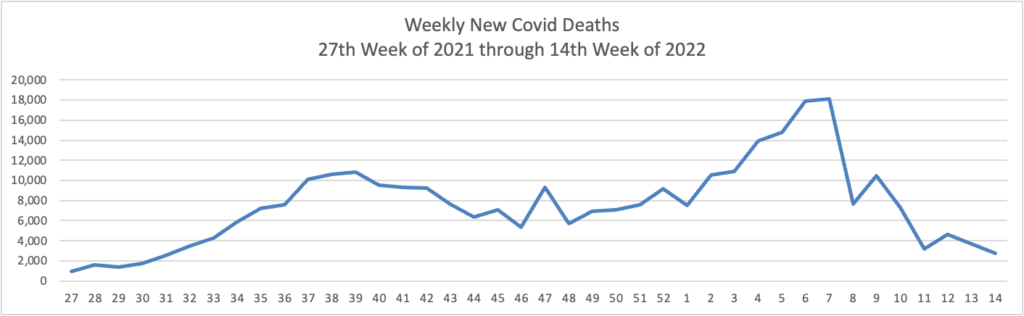
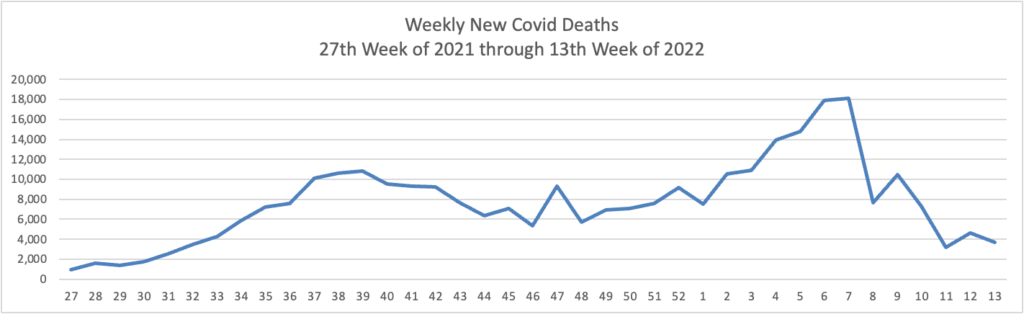
Epidemiologist David Dowdy of Johns Hopkins’ Bloomberg School of Public Health said that, despite the case increases, hospitalization and death rates overall remain relatively low compared with earlier periods in the pandemic — a reflection of how much immunity there is in the population.
“In some ways, this is encouraging, in that we’re starting to see a divergence between the number of cases and the number of hospitalizations and deaths,” Dowdy said. “But it’s also a little bit discouraging that we’ve been through all this and we’re still seeing a flat line and an uptick in the number of people getting admitted to the hospital and in people dying.”
In the FEHBlog’s view, the coordinator should stop fighting the Delta pandemic by focusing attention on better government distribution of Pfizer’s Paxlovid, which can cure the Omicron if taken timely. Kaiser Health News discusses this continuing and vexing distribution problem.
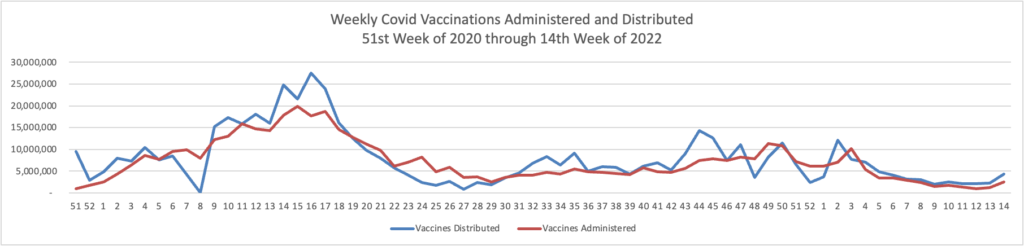
Unquestionably a need to focus attention on vaccinations and boosters remains essential. Govexec and Kaiser Health News ask why one-third of Americans over 65 have not received the first booster. Nearly all Americans over 65 are fully vaccinated. The article explains
People 65 and older account for about 75% of U.S. covid deaths. And some risk persists, even for seniors who have completed an initial two-dose series of the Moderna or Pfizer vaccine or gotten one dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. Among older people who died of covid in January, 31% had completed a first vaccination round but had not been boosted, according to a KFF analysis of CDC data
FEHB plans are well-positioned to help with this effort, given their demographics.
In other virus news, the American Hospital Association tells us
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention yesterday updated its testing guidance for clinicians treating children with hepatitis of unknown cause. The agency is investigating 109 potential hepatitis cases of unknown cause in U.S. children since last October, including five deaths. More than 90% of the patients were hospitalized, 14% received liver transplants and more than half had a confirmed adenovirus infection, but officials still don’t know the actual cause of their hepatitis and cautioned that it may take time to assess the evidence and learn more. Potential cases also have been reported in the United Kingdom and other countries.
Following up on last night’s hospital system merger news, Healthcare Dive reports
The Advocate Aurora Health and Atrium Health merger is likely to get a close review from the Federal Trade Commission as the Biden administration has taken a tougher stance on healthcare consolidation, antitrust and legal experts say. * * *
“I don’t think anything of this size in a healthcare transaction today is going to get rubber stamped,” said Bill Horton, a partner at Jones Walker who focuses on healthcare transactions. * * *
“Historically, the FTC concern in hospital and healthcare institution mergers has been the geographic overlap,” Horton said.
Advocate Aurora and Atrium do not have any geographic market overlap. The systems span six separate states through the Midwest and South.
“It doesn’t raise the same red flags, but it doesn’t mean that it gets waved through,” said Leemore Dafny, a Harvard Business School professor and former deputy director of healthcare and antitrust at the FTC.
The FTC is likely to examine whether the two systems negotiate with the same insurers even if they’re in different geographic locations, Dafny said.
From the interoperability front, Health Data Management offers an interesting take on government efforts to meet lofty public health goals for Data Modernization Initiative.
From the mental health care front, and to end on a high note, Health Payer Intelligence informs us
Consumers reported having positive experiences with their employer-sponsored mental and behavioral healthcare coverage during the coronavirus pandemic, a survey conducted on behalf of AHIP discovered.
“Health insurance providers are working every day to support Americans by helping them find the mental health support and counseling they need at a price they can afford,” Matt Eyles, president and chief executive officer of AHIP, said in a press release.