Thursday Miscellany

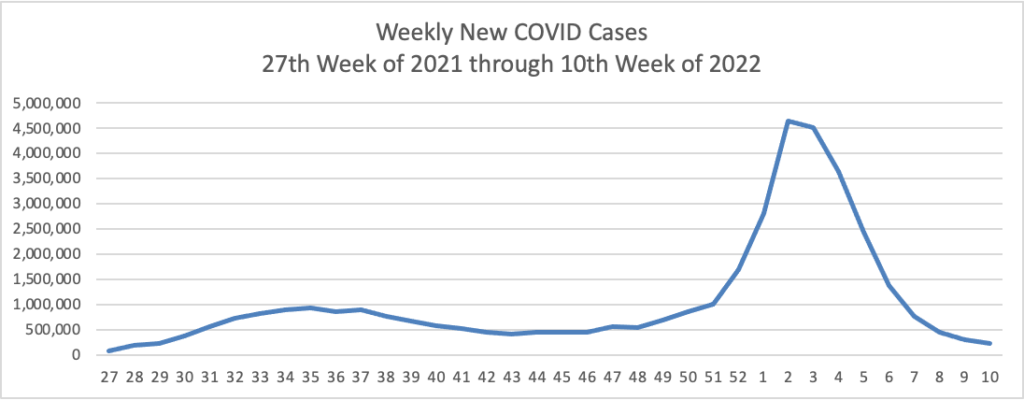
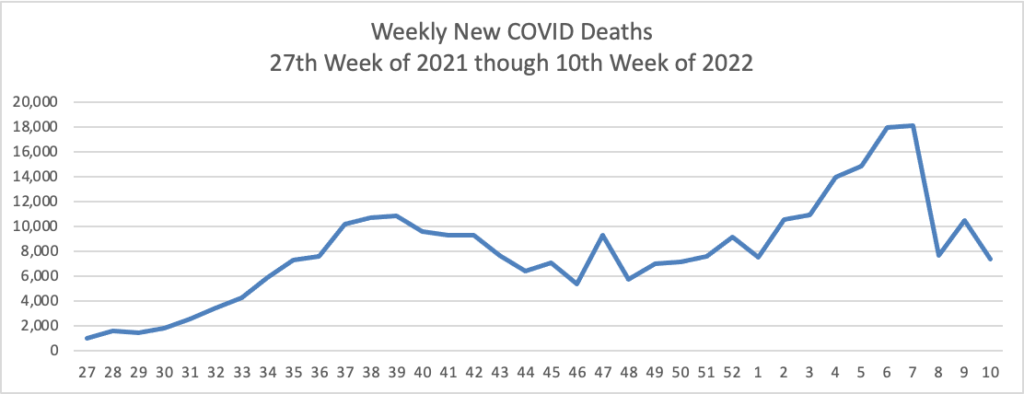
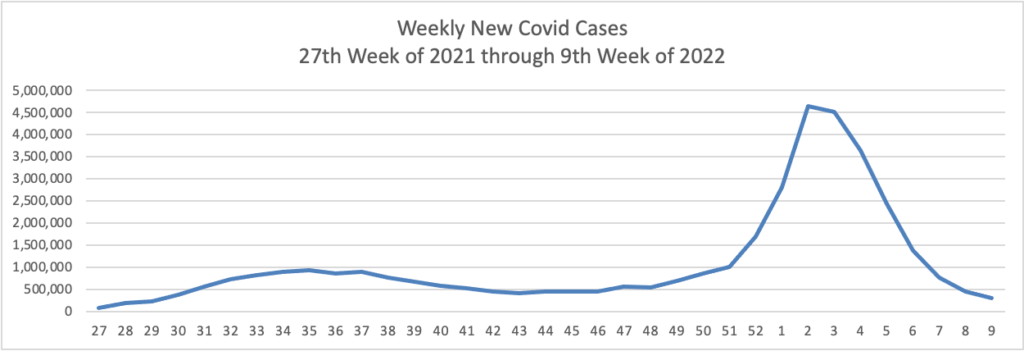
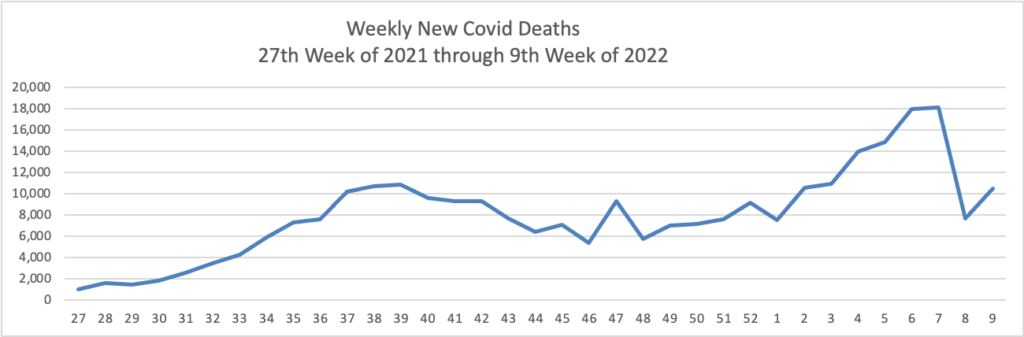
From the Omicron and siblings front, STAT News reports why “It’s not clear what will happen [with Covid] in the near future in the United States.”
Politico tells us
President Joe Biden announced Thursday that Ashish Jha will be the next White House Covid-19 response coordinator, installing a well-known public health commentator on the administration’s pandemic team.
Jha, the dean of Brown University’s School of Public Health, has been a regular guest across cable and network news throughout the Covid-19 pandemic. He will replace Jeffrey Zients, who has headed the Biden administration’s coronavirus response since January 2021 and will return to private life in April.
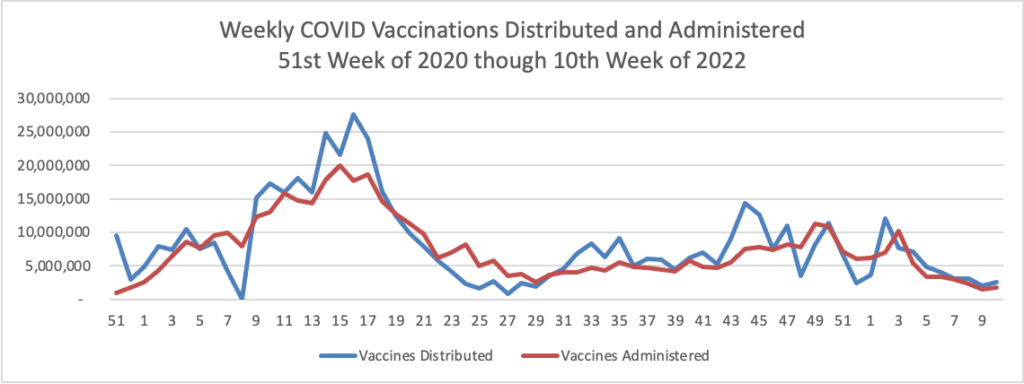
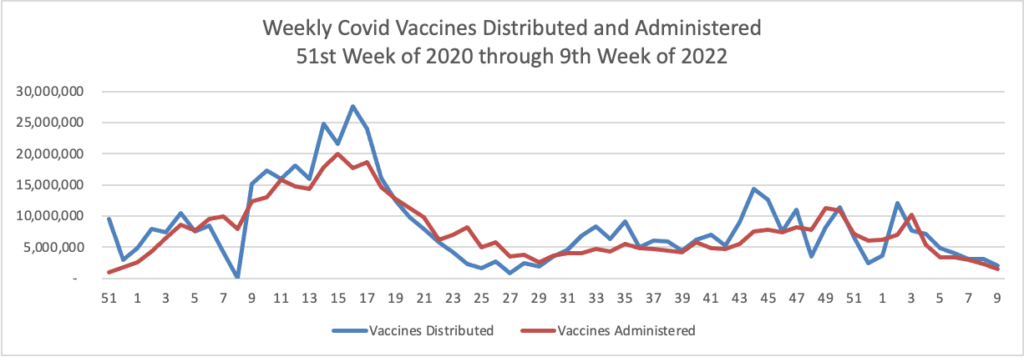
The Boston Globe reports “Moderna said late Thursday that it asked the Food and Drug Administration for emergency authorization of a second booster of its coronavirus vaccine for all adults, a significantly broader request than Pfizer and BioNTech filed for their shot this week.”
The White House also announced “launching the Clean Air in Buildings Challenge, a key component of the President’s Plan, that calls on all building owners and operators, schools, colleges and universities, and organizations of all kinds to adopt key strategies to improve indoor air quality in their buildings and reduce the spread of COVID-19. “
From the substance use disorder front, the American Medical Association informs us
CNN (3/16, McPhillips) reports, “Annual drug overdose deaths have reached another record high in the United States as deaths from fentanyl and other synthetic opioids surge to unprecedented levels,” investigators concluded. In fact, “an estimated 105,752 people died of drug overdoses in the 12-month period ending October 2021, according to provisional data published” March 16 by the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics.
From the public health front, the National Institutes of Health announced
Nearly 100,000 highly diverse whole genome sequences are now available through the National Institutes of Health’s All of Us Research Program. About 50% of the data is from individuals who identify with racial or ethnic groups that have historically been underrepresented in research. This data will enable researchers to address yet unanswerable questions about health and disease, leading to new breakthroughs and advancing discoveries to reduce persistent health disparities.
“Until now, over 90% of participants from large genomics studies have been of European descent. The lack of diversity in research has hindered scientific discovery,” said Josh Denny, M.D., chief executive officer of the All of Us Research Program. “All of Us participants are leading the way toward more equitable representation in medical research through their involvement. And this is just the beginning. Over time, as we expand our data and add new tools, this dataset will become an indispensable resource for health research.”
The genomic data is available via a cloud-based platform, the All of Us Researcher Workbench, and also includes genotyping arrays from 165,000 participants. Whole genome sequencing provides information about almost all of an individual’s genetic makeup, while genotyping arrays, the more commonly used genetic testing approach, capture a specific subset of the genome.
The FEHBlog does participate in All of Us surveys but took a pass on genome sequencing study.
From the healthcare business front, Beckers Payer Issues lets us know
UnitedHealth Group is mounting its defense against the Justice Department’s challenge to its proposed $13 billion acquisition of Change Healthcare, arguing the government’s case is “flawed.” * * *
“The government’s case rests entirely on speculation and theories unsupported by any past conduct, i.e., that Optum will somehow exploit Change Healthcare’s products and services to secure an unfair advantage for UnitedHealthcare’s health insurance business,” UnitedHealth said in its statement.
“Optum’s business model and financial success is dependent on providing products and services to external customers, not just UnitedHealthcare,” the company added. “Put simply, any misuse of customer [competitively sensitive information] would be economic suicide for Optum because its sophisticated external customer base would simply cease using Optum’s services and turn to any number of Optum competitors.”
The Justice Department also argued the acquisition would give UnitedHealthcare a monopoly in claims-editing technology, but UnitedHealth said it has agreed to divest the business and plans to ink a purchase agreement in “a matter of weeks.”