Tuesday’s Tidbits

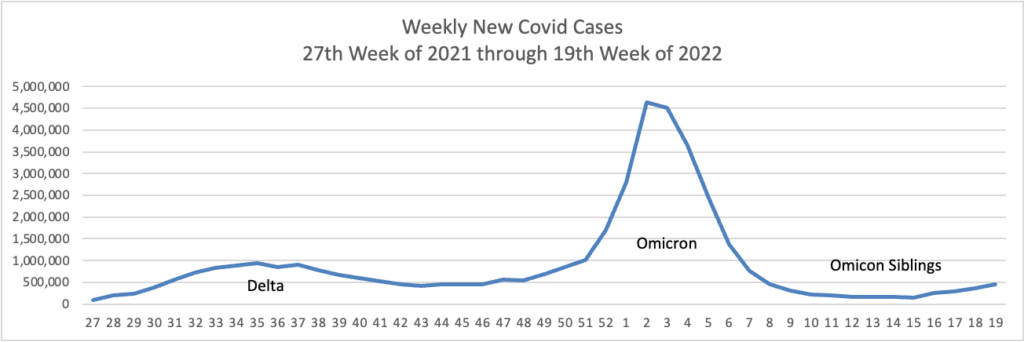
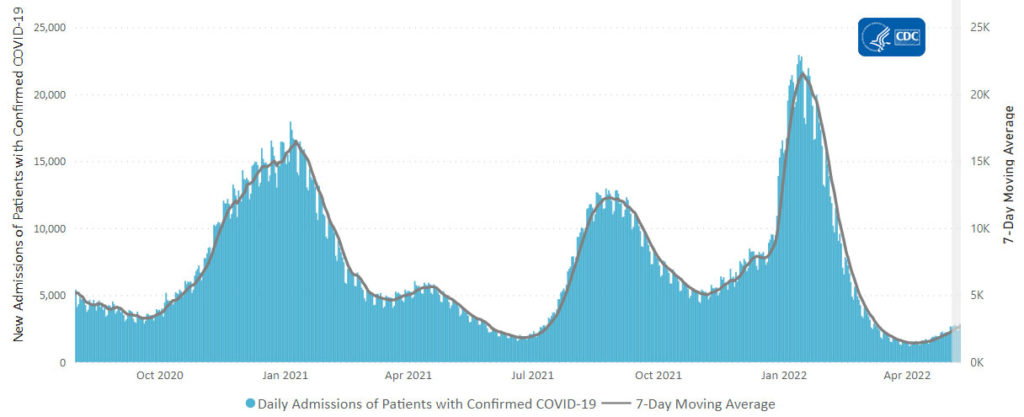
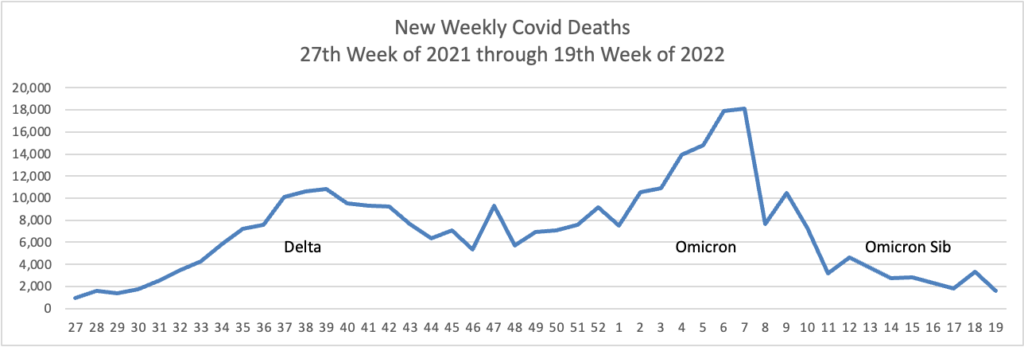
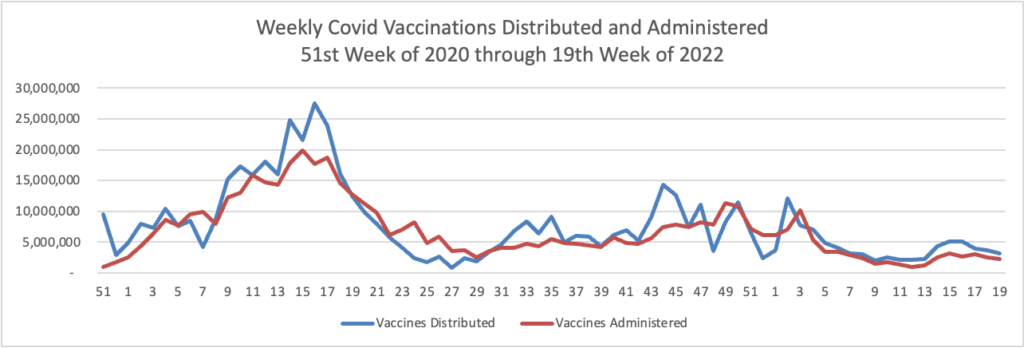
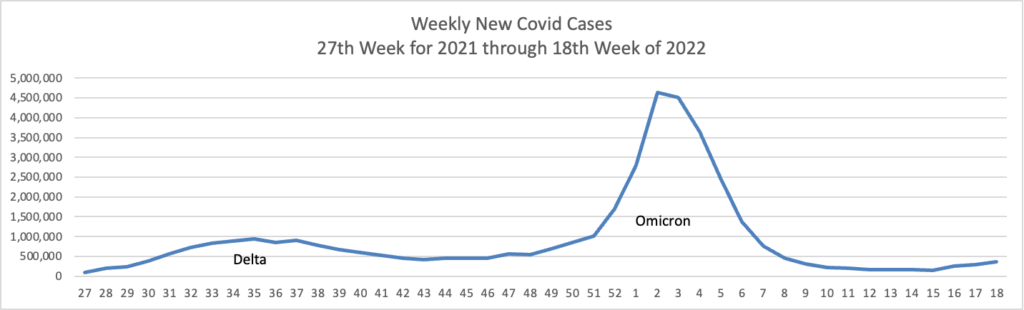
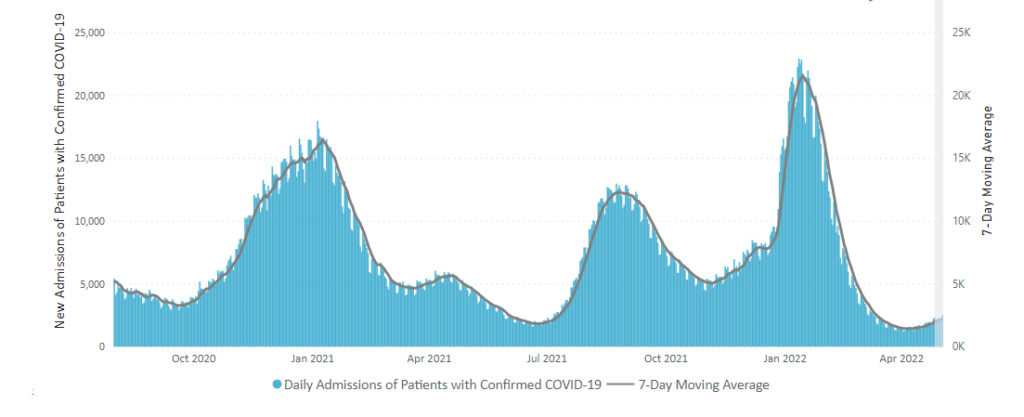
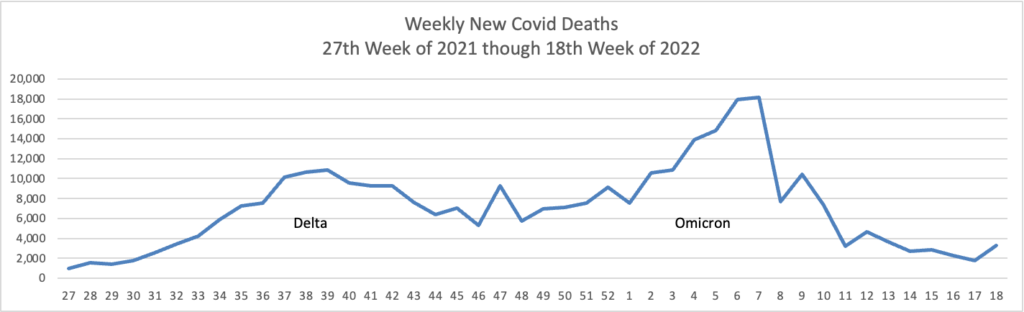
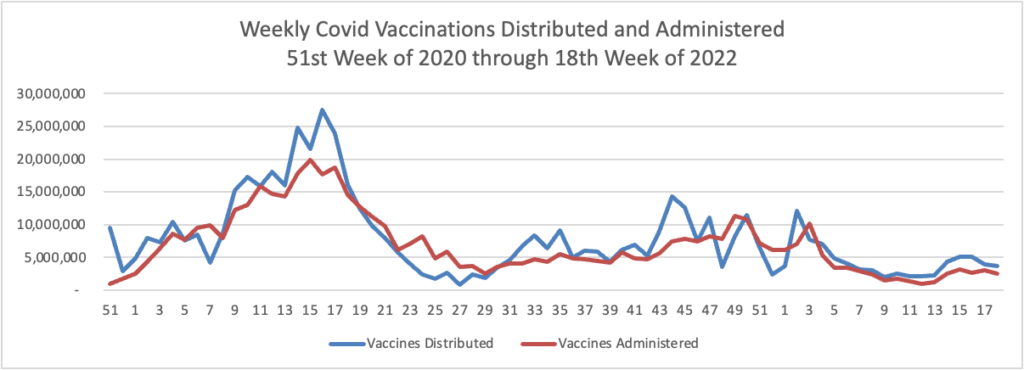
From the Omicron and siblings front —
The Secretary of Health and Human Services has extended the Covid public health emergency for another 90 days. Bloomberg explains, “The declaration allows the US to grant emergency authorizations of drugs, vaccines and other medical countermeasures, as well as administer those products to millions of people at no out-of-pocket cost. It’s also enabled millions of Americans to get health coverage through Medicaid, among other benefits.” Bloomberg’s sources expect the declaration to be renewed again in July 2022.
The American Hospital Association informs us
The Food and Drug Administration today authorized a single Pfizer COVID-19 booster dose for children aged 5-11 who completed the Pfizer vaccine primary series at least five months before. FDA authorized the vaccine for this age group last October.
“The FDA has determined that the known and potential benefits of a single booster dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine for children 5 through 11 years of age at least five months after completing a primary series outweigh its known and potential risks and that a booster dose can help provide continued protection against COVID-19 in this and older age groups,” said Peter Marks, M.D., director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
In public health news —
- The federal government’s Million Hearts campaign has launched a website discussing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The site explains “Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are a leading cause of maternal mortality and can put both mother and baby at risk for problems during pregnancy.1 High blood pressure can also cause problems during and after delivery. Importantly, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are often preventable and treatable.”
- The Centers for Disease Control has updated its website discussing diabetes and heart disease. The FEHBlog knows from his PCP about the dangerous relationship between those two diseases.
In survey news —
- Beckers Hospital Review relates that “The Lown Institute, a nonpartisan healthcare think tank, released its ranking May 17 of the best hospitals in the U.S. for avoiding overuse of low-value tests and procedures.”
- Fierce Healthcare tells us, “Utah is the healthiest state for seniors this year, earning high marks for low prevalence of smoking and excessive drinking, according to a new report from the United Health Foundation. The philanthropic arm of UnitedHealth Group issued its annual America’s Health Rankings senior report Tuesday morning, which highlights state-specific performance across a slew of measures as well as progress, or lack thereof, on several key health issues facing seniors.”
From the healthcare business front
Fierce Healthcare reports
Private insurance plans paid hospitals on average 224% more compared with Medicare rates for both inpatient and outpatient services in 2020, a new study found.
Researchers at RAND Corporation looked at data from 4,000 hospitals in 49 states from 2018 to 2020. While the 224% increase in rates is high, it is a slight reduction from the 247% reported in 2018 in the last study RAND performed.
“This reduction is a result of a substantial increase in the volume of claims in the analysis from states with prices below the previous average price,” the study said.
The report showed that plans in certain states wound up paying hospitals more than others. It found that Florida, West Virginia and South Carolina had prices that were at or even higher than 310% of Medicare.
But other states like Hawaii, Arkansas and Washington paid less than 175% of Medicare rates.
The American Hospital Association replies
The RAND Corporation’s latest hospital pricing report again “overreaches and jumps to unfounded conclusions based on incomplete data,” AHA President and CEO Rick Pollacksaid today. “The report looks at claims for just 2.2% of overall hospital spending, which, no matter how you slice it, represents a small share of what actually happens in hospitals and health systems in the real world. RAND also continues to ignore that hospitals are not all the same. Researchers should expect variation in the cost of delivering services across the wide range of U.S. hospitals — from rural critical access hospitals to large academic medical centers. Tellingly, when RAND added more claims as compared to previous versions of this report, the average price for hospital services declined. This suggests what we have long suspected: you simply cannot draw credible conclusions from such a limited and biased set of claims.
“Further, the results highlight what even the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) acknowledges: Medicare does not fully cover the cost of providing care to Medicare beneficiaries. Pinning commercial prices to inadequate Medicare rates would cause even more financial strain to hospitals already facing tremendous challenges as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and rising inflation. The result could be reduced patient access to care.”
I agree with the American Hospital Association that the problem is Medicare. Why Sen. Sanders continues to push Medicare for All is a mystery to the FEHBlog.
Also, Healthcare Dive informs us
Humana plans to open about 100 new value-based primary care clinics for Medicare patients between 2023 and 2025 through its second joint venture with private-equity firm Welsh, Carson, Anderson & Stowe, according to a Monday release from the payer.
The clinics will be managed and operated under Humana’s CenterWell Senior Primary Care brand, and WCAS will have majority ownership while Humana will have a minority stake.
The $1.2 billion expansion builds upon an existing venture with the same firm to open 67 clinics by early 2023.
From the Rx coverage front, Drug Channel reports on “The State of Specialty Pharmacy 2022: Reflections, Trends, and Photos from #Asembia22.”
I had the honor of presenting during the event’s general session: The Specialty Pharmacy Industry Update & Outlook. As in past years, I was joined by Doug Long from IQVIA.
You can download our full slide deck here: https://drugch.nl/asembia22.
From the mental healthcare front, Health Payer Intelligence discusses another angle considered in the UHG report on seniors mentioned above.
Over the last decade, seniors have experienced rising rates of mental healthcare needs, drug-related deaths, and early mortality, the UnitedHealth Foundation’s 2022 Senior Report shows.
“The 2022 Senior Report shows that the wellbeing of older adults was declining before the pandemic, which we know exacerbated many of these challenges,” Rhonda Randall, DO, executive vice president and chief medical officer of UnitedHealthcare Employer and Individual, said in the press release.
“We urge people to help the seniors in your lives reconnect with the communities and activities they have enjoyed in the past but may not yet have returned to. We are focused on reducing disparities in the health care system for everyone, including older Americans.”
In webinar news — The Labor Department is holding a virtual event on May 25 concerning building mental health-friendly workplaces.