Tuesday’s Tidbits

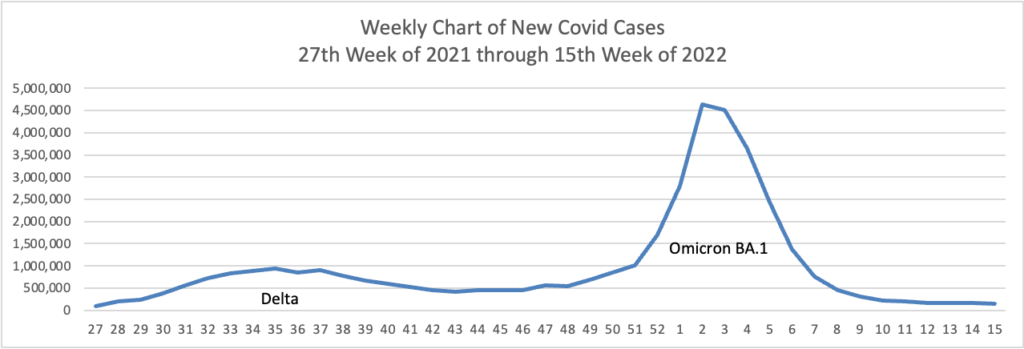
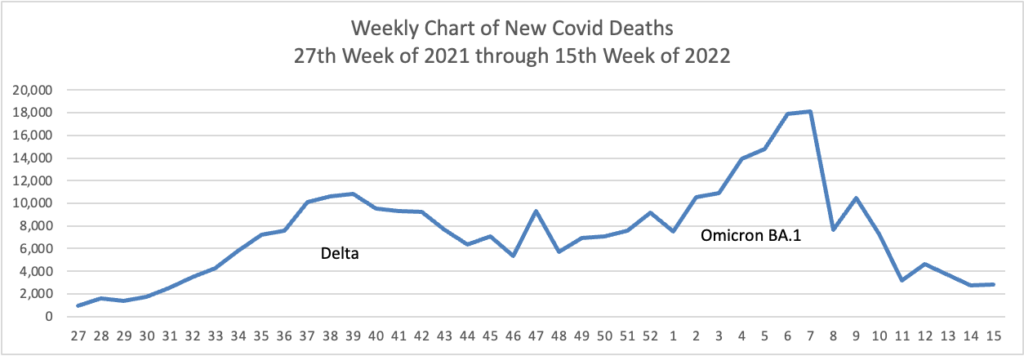
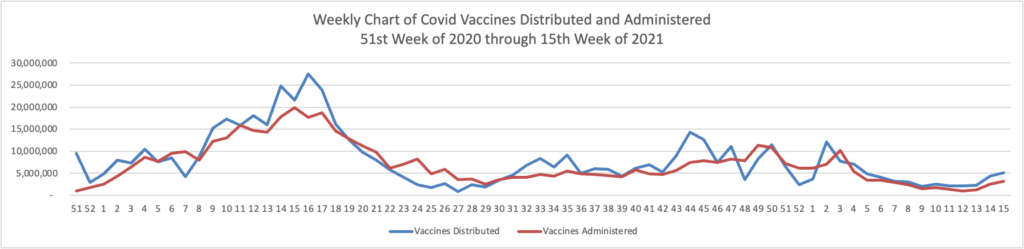
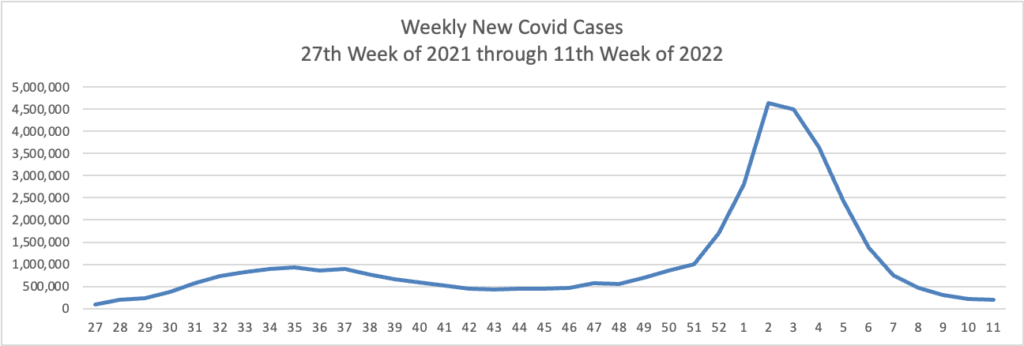
From the Omicron and siblings front
- The Wall Street Journal has updated its article on Covid boosters.
- The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) today released “a Final Evidence Report assessing the comparative clinical effectiveness and value of [specific] outpatient treatments for COVID-19 [, principally Pfizer’s pill Paxlovid and Merck’s pill molnupiravir ].
A majority (11-2) found current evidence is not adequate to demonstrate a net health benefit when molnupiravir is compared to symptomatic care alone.
All panelists (13-0) found that current evidence is adequate to demonstrate a net health benefit when Paxlovid is compared to symptomatic care alone.
Due to uncertainty in the net health benefit for molnupiravir, a majority of panelists voted that it represents “low-to-intermediate” long-term value for money.
A majority of panelists found that Paxlovid represents “high” long-term value for money.
- ICER presented at the OPM/AHIP carrier conference last month. ICER “is an independent non-profit research institute that produces reports analyzing the evidence on the effectiveness and value of drugs and other medical services. ICER’s reports include evidence-based calculations of prices for new drugs that accurately reflect the degree of improvement expected in long-term patient outcomes, while also highlighting price levels that might contribute to unaffordable short-term cost growth for the overall health care system.”
- Speaking of the Covid pills, STAT News discusses the use of telehealth services to prescribe them. The upshot, as the FEHBlog understands it, is while using telehealth for this purpose is convenient for patients, experts are unsure whether the telehealth service provides adequate follow-up care to the patient.
Also, from the Rx coverage front, the Food and Drug Administration issued a news roundup today.
From the healthcare business front, BioPharma Dive reports
Pfizer has agreed to acquire Biohaven Pharmaceuticals for $11.6 billion in a deal that turns an existing alliance on a fast-selling migraine drug into a big bet on its future growth.
Pfizer will pay $148.50 per share in cash for each Biohaven share it doesn’t already own, representing a roughly 79% premium to the company’s Monday closing price and a 33% premium to its average share price of $111.70 over the last three months. The deal, which is expected to close early next year, is by far the biggest biotech buyout of 2022, according to data compiled by Biopharma Dive.
Announced Tuesday, the acquisition hands Pfizer full rights to Nurtec ODT, a pill that’s approved in the U.S. and other countries for the treatment and prevention of migraines. Biohaven’s pipeline also includes an experimental nasal spray for migraines, zavepegant, that’s been submitted to U.S. regulators, as well as five additional, preclinical treatments that block the same protein target.
From the mental health parity front, the Labor Department’s Employee Benefits Security Administration announced that the agency will be holding a mental health parity compliance assistance webcast on May 24 from 2-3 pm ET. Here is a link to the announcement which explains how to register for the webcast.
From the patient safety front, the Leapfrog Group “released the spring 2022 Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade, which assigns a letter grade to nearly 3,000 U.S. general hospitals based on over 30 measures of patient safety.”
At HospitalSafetyGrade.org, the public can find detailed information about a hospital’s performance on patient experience and other safety measures used to grade hospitals.
Across all states, highlights of findings from the spring 2022 Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade include:
Thirty‐three percent of hospitals received an “A,” 24% received a “B,” 36% received a “C,” 7% received a “D,” and less than 1% received an “F.”
Five states with the highest percentages of “A” hospitals are North Carolina, Virginia, Utah, Colorado, and Michigan.
There were no “A” hospitals in Wyoming, West Virginia, the District of Columbia, or North Dakota.
From the medical research department, Medscape informs us
Eight modifiable risk factors were linked to more than one in three cases of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia in the U.S., a cross-sectional analysis showed.
The eight risk factors — midlife obesity, midlife hypertension, physical inactivity, depression, smoking, low education, diabetes, and hearing loss — were associated with 36.9% (95% CI 36.5-37.3) of Alzheimer’s and dementia cases, reported Roch Nianogo, MD, PhD, of the University of California Los Angeles, and Deborah Barnes, PhD, MPH, of the University of California San Francisco, and co-authors.
The factors most prominently associated with Alzheimer’s and dementia were midlife obesity, at 17.7% (95% [Confidence Interval] CI 17.5-18.0); physical inactivity, at 11.8% (95% CI 11.7-11.9); and low educational attainment, at 11.7% (95% CI 11.5-12.0).
“We published a similar study a little more than 10 years ago, and the most important risk factors then were physical inactivity, depression, and smoking,” Barnes told MedPage Today.
“Today, the top three risk factors are midlife obesity, physical inactivity, and low education,” she observed. “This is important because it suggests that the growing number of people who are obese in the U.S. could have a major long-term impact on dementia rates.”
From the clarification front, the FEHBlog often reminds folks that federal employees who retired under the Civil Service Retirement System before 1984 are not eligible for free Medicare Part A. The FEHBlog dug into this issue today, and he discovered this 2013 Reg Jones Q&A on this topic that the Federal Times published.
Q. I retired in 2009 under CSRS. I am close to 65, and the answer to one of the questions asked states that people in CSRS are not eligible for Medicare because they didn’t pay into Social Security.
I was in CSRS before the change to FERS and stayed with CSRS. I had Medicare deductions taken from my pay from 1983-84 till I retired in 2009.
Do the Medicare funds I paid since 1983 make me eligible for Medicare or just part of it?
So which is right? I need to know so I can do what needs to be done — enroll or not. I’m currently insured under federal BCBS.
A. CSRS employees who retired before Dec. 31, 1983, aren’t eligible for Medicare Part A. Nor are CSRS employees who retired after that date but before having Medicare deductions taken from their pay for 10 years.
On the other hand, they are eligible to enroll in Medicare Part B, which is open to everyone 65 or older.
Consequently, the cadre of 65 and older federal annuitants without Medicare A is larger than the FEHBlog understood. This cadre is relevant to the Postal Reform Act because that law keeps Postal annuitants over aged 65 without Medicare Part in the legacy FEHBP.