Tuesday Tidbits

Roll Call reports from Capitol Hill
More than 3.5 million veterans who were exposed to toxic substances on overseas deployments will gain easier access to health and disability benefits under a bill that cleared the Senate Tuesday.
President Joe Biden is certain to sign the bill into law in the coming days.
The bill would make servicemembers who contracted any of 23 conditions — from brain cancer to hypertension — after being deployed to Iraq, Afghanistan and other combat zones automatically eligible for VA benefits. The measure is expected to cost nearly $280 billion over a decade, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
This law should save the FEHB Program money as the federal workforce has a large cadre of veterans who use veterans’ healthcare. VA facilities charge the FEHB and private sector plans for non-service connected health care. This law confirms that toxic substances treatment to service-connected care for which the VA is liable.
Govexec adds
The [VA] bill [also] authorizes leases for 31 new medical facilities at VA to help accommodate the expected surge in patients, which is expected to cost nearly $1 billion. The Congressional Budget Office found the slew of pay and other human resources changes would come with a $5.7 billion price tag over the next decade.
The bill will authorize the department to buy out the contract of health care professionals to recruit them to VA, so long as they make a four-year commitment to the department. VA will have $40 million per year for the buyouts. VA’s health care employees will be eligible for pay boosts worth 50% of their base salaries, up from the current cap of 30%. Overall pay would be capped at level two of the Executive Service pay scale, which is currently $203,000 per year. McDonough has called lifting the pay caps essential for VA’s recruiting and retention efforts and has aggressively pushed Congress to pass the reform.
With regard to the Schumer-Manchin reconciliation bill, the Hill reports that Senators Manchin and Simema are exchanging text on the bill.
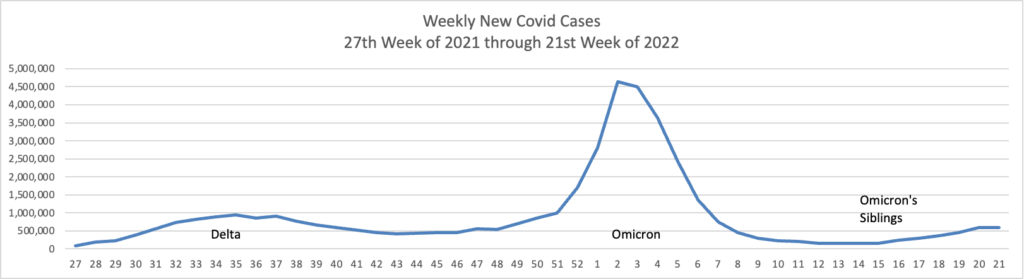
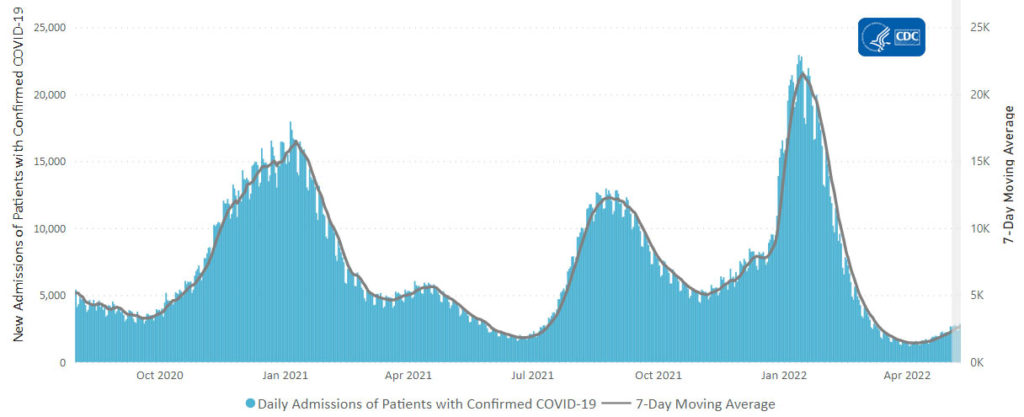
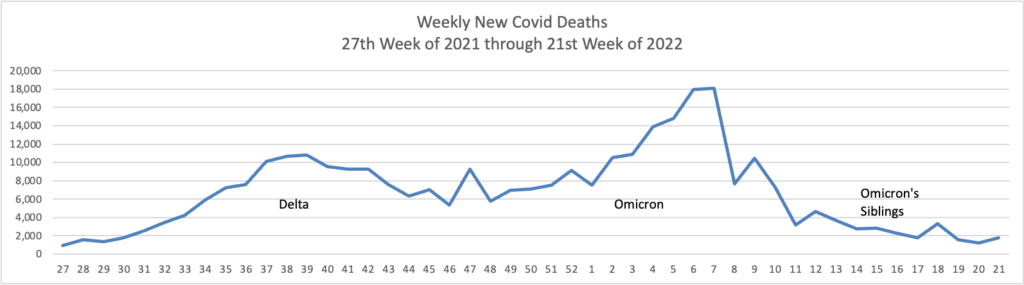
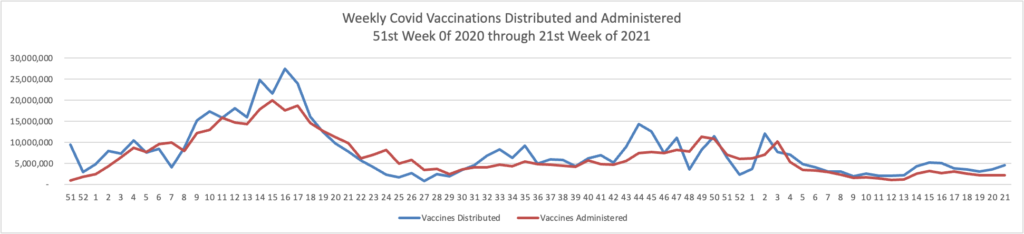
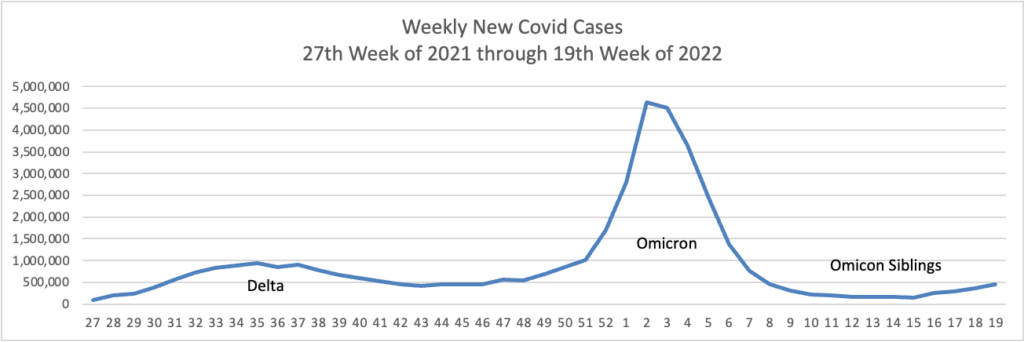
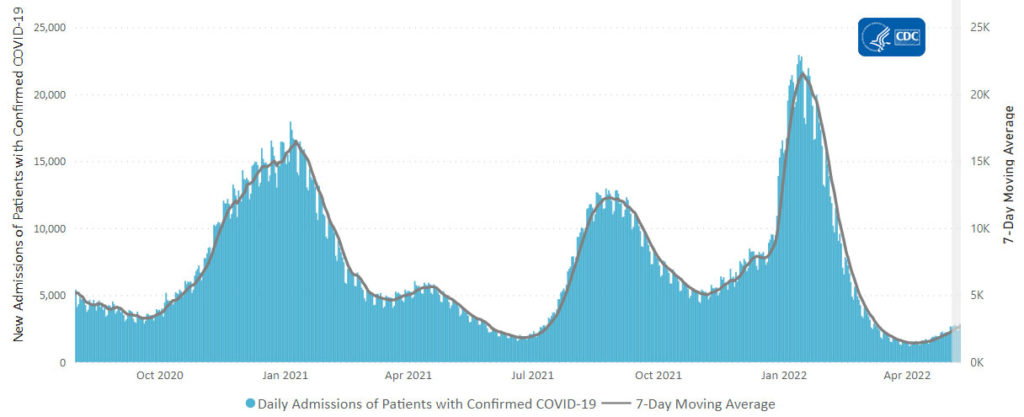
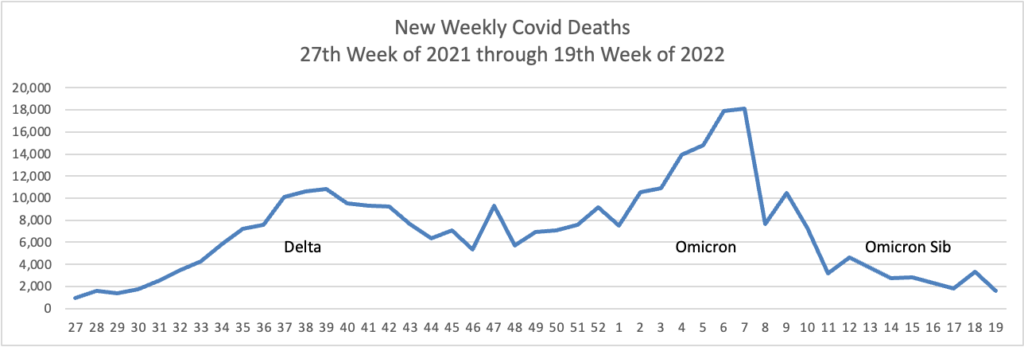
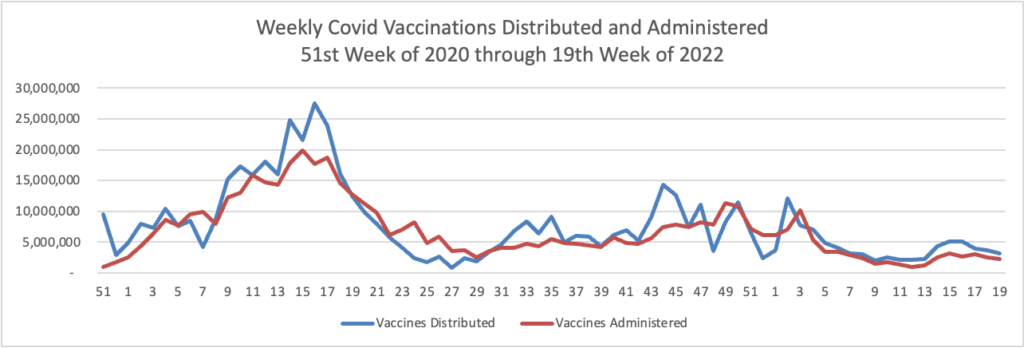
From the Omicron and siblings front,
McKinsey and Company offer their assessment of when the Covid pandemic will end.
In this update, we discuss the outlook, the current and potential future use of boosters and therapeutics, and the shifts in response strategies to the COVID-19 crisis around the world. We also introduce the McKinsey COVID-19 Immunity Index—a tool for understanding a community’s current level of risk from the disease.
A group of physicians provides their observations in MedPage Today on how best to investigate the Paxolovid rebound issue.
The debate about “COVID-19 rebound” after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) treatment is one of these timely areas warranting further investigation. Continuing down the current path of uncertainty has consequences for how and by whom this antiviral should be used. However, by applying lessons learned from the early days of the pandemic — including acknowledging the importance of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) — we can avoid repeating the same mistakes. To do this, it is necessary to start by defining the question, identifying current knowledge gaps, and only then can one propose scientific solutions to bring a rapid resolution to the COVID-19 rebound controversy.
Paxlovid consists of two drugs: nirmatrelvir, which inhibits a SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibiting viral replication, and ritonavir, which slows the inactivation and breakdown of nirmatrelvir. Per a CDC health advisory released in May, COVID-19 rebound is defined as a return of symptoms or a “new positive viral test after having tested negative” occurring “2 to 8 days after initial recovery.” We just saw this over the weekend in the case of President Biden.
This definition of rebound is challenging and prone to inflating the incidence of rebound. It is possible some individuals identified as having “Paxlovid rebound” may have been experiencing a waxing and waning of COVID-19 symptoms while some unknown number of other reported rebound cases could be due to the known limitations of COVID-19 testing.
Precision Vaccinations tells us that in the near future the federal government will make the Omicron antibody based treatment known as Evusheld available through local pharmacies including “Albertsons, Acme, Jewel-Osco, Pavilions, Randalls, Safeway, Star Market, Vons, CPESN, Amber Specialty Pharmacy, Managed Healthcare Associates, and Thrifty White.”
Hugh Montgomery, Professor of Intensive Care Medicine at University College London, UK, and TACKLE principal investigator, commented in a press release, “Despite the success of vaccines, many individuals such as older adults, individuals with co-morbidities, and those who are immunocompromised, remain at risk for poor outcomes from severe COVID-19.”
“Additional options are needed to prevent disease progression and reduce the burden on healthcare systems, especially with the continued emergence of new variants.”
“The TACKLE (study) results show that one intramuscular dose of Evusheld can prevent these individuals from progressing to severe COVID-19, with earlier treatment leading to even better results.”
From the moneypox front, Fierce Healthcare reports
The White House has named Robert Fenton to serve as the response coordinator for the monkeypox outbreak, as calls for a larger federal role intensify.
Fenton previously helped to coordinate COVID-19 vaccine distribution while working at the Federal Emergency Management Agency. He will work alongside Demetre Daskalakis, M.D., who will be the deputy coordinator.
The coordinators will lead the administration’s efforts on “strategy and operations to combat the current monkeypox outbreak, including equitably increasing the availability of tests, vaccinations and treatments.”
From the Affordable Care Act front, the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans informs us
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has issued Revenue Procedure 2022-34 providing the indexing adjustment for the required contribution percentage. For plan years beginning in 2023, the required contribution percentage is 9.12%, down from 9.61% in 2022.
The affordability calculation can determine whether an individual can afford employer-sponsored health coverage and affect whether the individual would be eligible for a premium tax credit on the health insurance exchanges. This could affect employers that do not use a safe harbor method to determine whether the coverage they offer is affordable to employees.
For plan years beginning in 2023, employer-provided coverage is considered affordable for an employee if the employee required contribution is no more than 9.12% of that employee’s household income. Because applicable large employers generally do not know their employees’ household incomes, there are three safe harbor methods for calculating affordability.
In the FEHB Program, OPM must assure itself that the lowest premium nationwide FEHB plan premium for the self only option does not cost more than 9.12% of the lowest paygrade federal employee eligible to participate in FEHBP.
From the FEHB front, Fedweek columnist Reg Jones wraps up his series of federal employee and annuitant survivor benefits.
From the Medicare front, Healthcare Dive reports on provider reaction to yesterday’s final CMS rule on Medicare Part A payments to inpatient hospitals beginning October 1, 2022.
Providers remained largely unhappy early this week despite a final ruling issued by the CMS on Monday that increases inpatient payments to hospitals by more than was initially proposed.
Organizations like The American Hospital Association said it was “pleased” by the payment update, a 4.3% bump up from the proposed 3.2%, but added it “still falls short of what hospitals and health systems need to continue to overcome the many challenges that threaten their ability to care for patients and provide essential services for their communities.”
Group purchasing organization Premier agreed, saying the payment update “falls woefully short” of what is needed for health systems. “Coupled with record high inflation, this inadequate payment bump will only exacerbate the intense financial pressure on American hospitals,” SVP of Government Affairs Soumi Saha said in a statement.
Beckers Hospital review offers six takeaways from the final rule.
From the U.S. healthcare business front
Healthcare Dive reports
High operating expenses took their toll on hospitals and physician groups in June, producing negative year-over-year margins for a sixth consecutive month, a new report from Kaufman Hall found. Month-to-month increases in patient volumes were not enough to offset the growing cost of care, the advisory firm said Monday.
Compared with May, operating margins improved, contract labor costs fell as demand slowed, and expenses cooled slightly in the latest month. But the industry has yet to turn the corner on an “enormously difficult year,” the report said.
“Although hospitals are seeing improved volumes and reduced expenses month-over-month, they will likely end up with historically low margins for the remainder of the year,” Kaufman Hall predicted.
Louisiana-based Ochsner Health has officially merged with Rush Health Systems, giving the merged system seven hospitals and more than 30 clinics in the east Mississippi and west Alabama region, according to a Monday release.
New names and branding are being rolled out at regional hospitals under the new brand, Ochsner Rush Health, the release said. Ochsner Rush Health will have 250 staff and contracted physicians and 95 advanced practice providers.
Ochsner Rush Health is also boosting its minimum wage to $12 an hour, impacting more than 400 employees and representing a $1.5 million investment, according to the release.
From the public health front,
- Healio offers a bleak outlook for chronic disease in the US over the next forty years “likely stressing an already burdened health care system.”
- The Center for Disease Control points to its revamped diabetes website “for people with diabetes or who are at risk for diabetes, and their families and friends.”
From the judicial front,
STAT News tells us
In a significant victory for AbbVie, a U.S. appeals court panel declined to revive a lawsuit that accused the company of using a so-called patent thicket to forestall competition for its Humira medication, a franchise product that generates billions of dollars in sales each year.
The opinion shot down arguments by unions, insurers, and the city of Baltimore, which alleged that AbbVie “abused the patent system” and “erected significant barriers to entry to block biosimilar competition” by filing dozens of patents for the drug. Some of the 132 U.S. patents that the company holds on its medicine extend to 2034, although the basic patent expired in 2016.
The case has been closely tracked over concerns that the use of numerous patents — some of which may offer only marginal improvements or changes to a medicine — are exploited by pharmaceutical companies to protect monopolies at the expense of consumers. This has prompted the Food and Drug Administration and Patent and Trademark Office to jointly examine the issue.
Congress can change the patent system applicable to prescription drugs.
The American Hospital Association reports
The Department of Justice today filed a lawsuit challenging an Idaho law restricting abortion. The complaint seeks a declaratory judgment that the law conflicts with and is preempted by the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act in situations where an abortion is necessary stabilizing treatment for an emergency medical condition. It also seeks an order permanently enjoining the law to the extent it conflicts with EMTALA, which requires hospitals that receive federal Medicare funds to provide necessary stabilizing treatment to patients who arrive at their emergency departments while experiencing a medical emergency.
The FEHBlog hopes that the federal court hearing the case seeks a decision from the Idaho Supreme Court on the scope of Idaho’s abortion law before proceeding with the case. The FEHBlog finds it hard to believe that any U.S. court would interpret its state’s abortion law as overriding obligations created by EMTALA and for that matter the Hippocratic Oath.