From Washington D.C., Roll Call tells us
The federal government will run out of cash to pay all its bills sometime between July and September unless the statutory debt limit is lifted, the Congressional Budget Office [CBO] warned Wednesday.
The report by the nonpartisan budget scorekeeper could put pressure on a divided Congress to reach a deal to increase, or at least suspend, the debt limit before adjourning for the annual August recess.
[A] separate CBO report issued Wednesday underscores the challenges for both parties in making the math add up. Deficits over the next decade are now projected to grow by $3.1 trillion, or 20 percent, during the next decade from the agency’s forecast last May.
STAT News “sat down with AMA President Jack Resneck on the sidelines of the [AMA’s Washington., D.C.] conference to talk about legislative reforms, physician burnout, and where the doctors’ lobby goes from here.” The Q&A made the FEHBlog crack up
What is the AMA stance on implementation of the law to end surprise medical bills for patients?
There’s a lot about the way those [HHS] rules were first written that went way outside of congressional intent. They put major thumbs on the scale of basically moving towards the insurers’ notion of what that value should be.
There’s so many things about those rules that basically would encourage insurers to either just say “Oh, I can pay so much less through this arbitration system that I’m just going to purposely not contract with any physicians” … or just unilaterally, dramatically lower payment rates in a way that threatens practices.
What nonsense!
Medical Economics shares a letter to Congress from a group of medical associations on the topic of value-based care.
The National Academies issued a report on “Achieving Whole Health.”
Whole health is physical, behavioral, spiritual, and socioeconomic well-being as defined by individuals, families, and communities. Whole health care is an interprofessional, team-based approach anchored in trusted relationships to promote well-being, prevent disease, and restore health. It aligns with a person’s life mission, aspiration, and purpose. It shifts the focus from a reactive disease-oriented medical care system to one that prioritizes disease prevention, health, and well-being. It changes the health care conversation from “What’s wrong with you?” to “What matters to you?”
The Office of Personnel Management released
its inaugural report: Government-wide DEIA: Our Progress and Path Forward to Building a Better Workforce for the American People. This report highlights accomplishments aligned with the Government-wide Strategic Plan to Advance DEIA in the Federal Workforce and preview priorities for 2023 consistent with Executive Order (EO) 14035.
“Whether you want to cure diseases, protect and preserve our national parks, combat climate change, or embark on missions to discover new galaxies, the Federal government is full of opportunity for the best and brightest to serve our country,” said OPM Director Kiran Ahuja. “In order to recruit and sustain the best talent, we must ensure every service-minded individual feels welcome and supported in contributing their talents to the Federal workforce. This inaugural report highlights progress made to advance diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility in the workplace, and we look forward to continuing the work to break down barriers to serve and help build a Federal government that draws from the strength and diversity of its people.”
Tomorrow, February 16, at 10 am ET, the Senate Commerce, Science, and Transportation Committee will hold a hearing titled “Bringing Transparency and Accountability to Pharmacy Benefit Managers.”
This hearing will address how the “Pharmacy Benefit Manager Transparency Act” will bring transparency into PBM business practices and prohibit unfair or deceptive PBM conduct that drives up costs for consumers. The bipartisan S. 127, Pharmacy Benefit Manager Transparency Act of 2023, was introduced by Chair Cantwell and Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), on January 27, 2023.
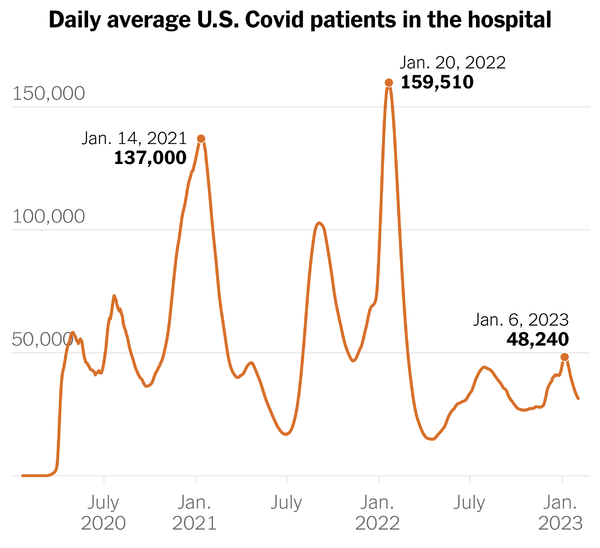
From the Omicron and siblings front —
STAT News reports
In an unexpected shift, Moderna has decided not to ask Americans to pay for its Covid-19 vaccine, a move that follows intense criticism over initial plans to charge $110 to $130 per dose after the company pivots from government contracts to commercial distribution.
The vaccine maker released a brief statement that it “remains committed” to ensuring everyone in the U.S. has access to its Covid-19 shot, regardless of whether they have health insurance coverage. For those lacking sufficient insurance, the company will tap a patient assistance program. “Everyone in the U.S. will have access to Moderna’s Covid-19 vaccine regardless of their ability to pay,” the company said.
The about-face came on the same day that Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), who chairs the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions, accused the company of “corporate greed” and scheduled a hearing next month to examine the initial decision to charge Americans for its Covid-19 shot. Moderna Chief Executive Officer Stéphane Bancel is among those expected to testify. * * *
A spokesman for America’s Health Insurance Plans, an industry trade group, suggested that health insurers will still get a bill. He sent a note saying the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (which advises the CDC) recently updated its list of recommended Covid vaccines and that, while beneficiaries pay nothing in cost sharing after commercialization, health plans are picking up the full cost.
No doubt about the validity of AHIP’s point.
Medscape notes, “The increased risk for diabetes following COVID-19 infection has persisted into the Omicron era, but vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 appears to diminish that likelihood, new data suggest.”
From the public health front —
- The White House announced
- “the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) released a new report that shows that the number of Americans with medical debt on their credit reports fell by 8.2 million from the first quarter of 2020 to the first quarter of 2022. Today’s report is consistent with a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that found that the number of Americans who are part of families having trouble paying their medical bills declined by 5.5 million between 2020 and 2021. One driver of these declines is the significant increase in the number of insured Americans over this period, a result of the President’s strategy of protecting and strengthening the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and lowering health care costs. The decline also reflects continued actions by the CFPB to highlight problems with inaccurate reporting of debt in collections and put the industry on notice to correct their behavior.”
- The Wall Street Journal reports “More older women with low-risk breast cancer could forgo radiation after surgery to avoid further side effects and costs, research showed, as some doctors work to limit tough treatments without hurting survival.” STAT News also offers an article on this topic.
- The National Cancer Institute posts on a variety of cancer topics. For example
- “The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tucatinib (Tukysa) with trastuzumab (Herceptin) to treat HER2-positive advanced colorectal cancer. The approval was based on the MOUNTAINEER trial, in which nearly 40% of participants’ tumors shrank after receiving the drugs.”
In other health care cost news —
Beckers Payer Issues relates
Employer-sponsored plans pay much higher rates for physician-administered drugs than Medicare, a research letter published Feb. 10 in JAMA Health Forum found.
Researchers at the Healthcare Cost Institute compared per-unit prices for the 10 most expensive and 10 most common physician-administered drugs from 2016 to 2020.
For the most commonly used drugs, employer-sponsored plans paid prices up to 3,350 percent higher than Medicare. For midazolam, employer-sponsored plans paid 30 times more than Medicare for the same drug, and they paid 20 times more for ondansetron.
For the most expensive drugs, employer-sponsored plans did not pay as extreme markups, the researchers found. Markups were 54 percent more than Medicare at the high end, and employer-sponsored plans paid similar prices to Medicare rates for some drugs.
Read the full study here.
Thank heavens OPM is allowing FEHB plans to offer Medicare Part D EGWPs for the Medicare prime members next year.
Health Payer Intelligence informs us “Out-of-pocket costs for buprenorphine prescriptions for opioid use disorder treatment decreased between 2015 and 2020, but costs varied by payer, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.”
From the U.S. healthcare business front
Beckers Payers Issues advises
The nation’s largest payers have filed their fourth quarter earnings reports, revealing which have the most U.S. commercial members.
Commercial includes fully- and self-insured members
Commercial enrollment rankings in 2022:
- Elevance Health: 31.4 million
- UnitedHealth Group: 26.7 million
- Cigna: 22 million
- CVS Health (Aetna): 17 million
- Centene: 2.5 million
- Humana: 986,000
Healthcare Dive reports
- After more than two decades together, CommonSpirit Health and AdventHealth are dissolving their joint venturemanaging hospital operations in Colorado and western Kansas.
- The management company, Centura, operates one of the largest hospital networks in the region, with 20 hospitals and a network of outpatient practices.
- In a release on Tuesday, the systems said the partnership had reached its “natural maturity.” CommonSpirit and AdventHealth didn’t lay out a timeline for the transition.
and
Elevance has closed its deal to acquire specialty pharmacy BioPlus, the insurer announced Wednesday, after first announcing the buy in November 2022.
The acquisition builds off the Indianapolis-based insurer’s promise to acquire companies around its health services business, with Elevance CEO Gail Boudreaux announcing at a November industry conference that the insurer planned to grow “very aggressively” into adjacent care services.
Beckers Hospital Review tells us
Walgreens has agreed to buy the assets of defunct digital pharmacy Medly for $19.35 million, according to a bankruptcy court filing.
Medly declared bankruptcy in December, months after its founder stepped down and it laid off more than half its staff. A judge approved the acquisition of Medly’s assets, including its files, inventory and intellectual property, Feb. 7 in U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware.
Medly raised $100 million in 2020, positioning itself as a digital competitor to retail pharmacies such as Walgreens and CVS.