Friday Stats and More
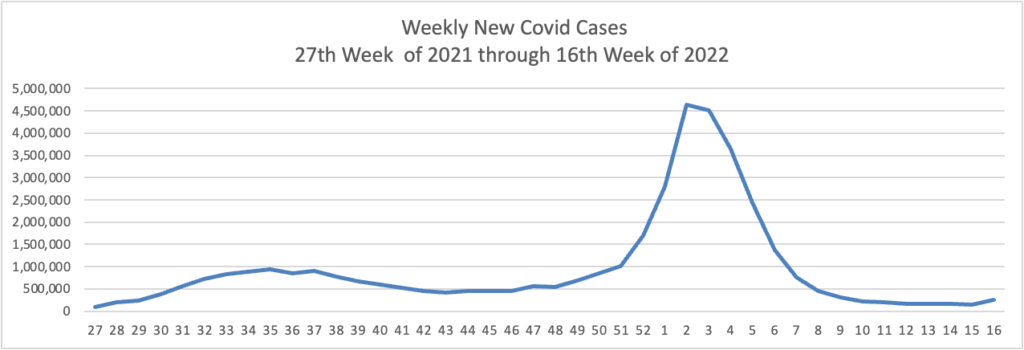
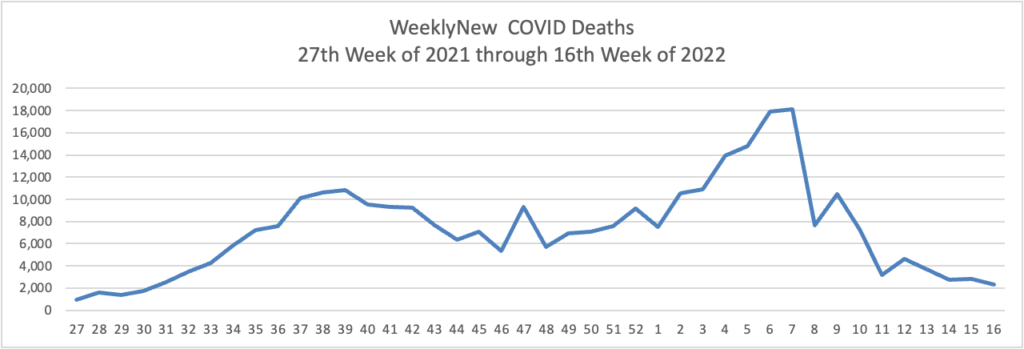
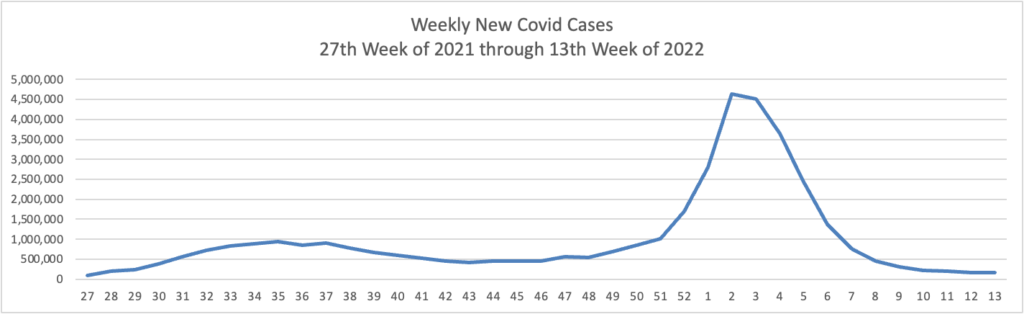
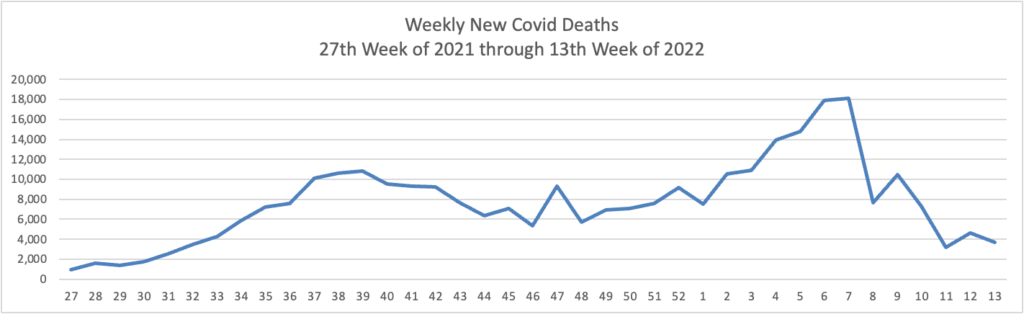
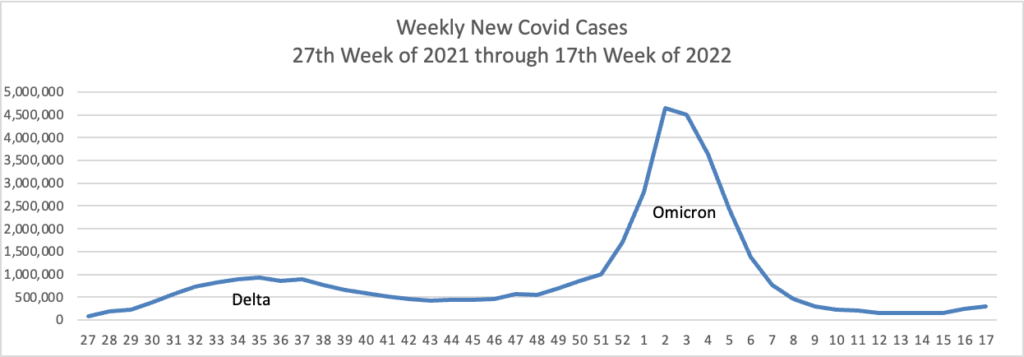
Based on the Centers for Disease Control’s Covid Data Tracker and using Thursday as the first day of the week, here are the FEHBlog’s weekly charts of new Covid cases and deaths from the 27th week of 2021 through the 17th week of 2022:
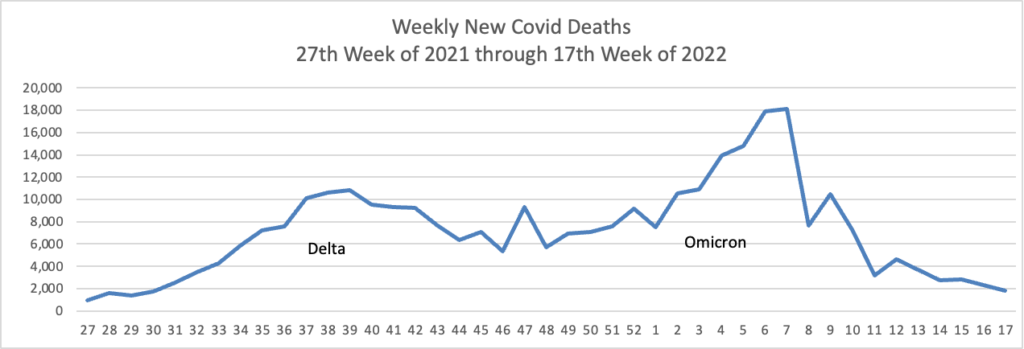
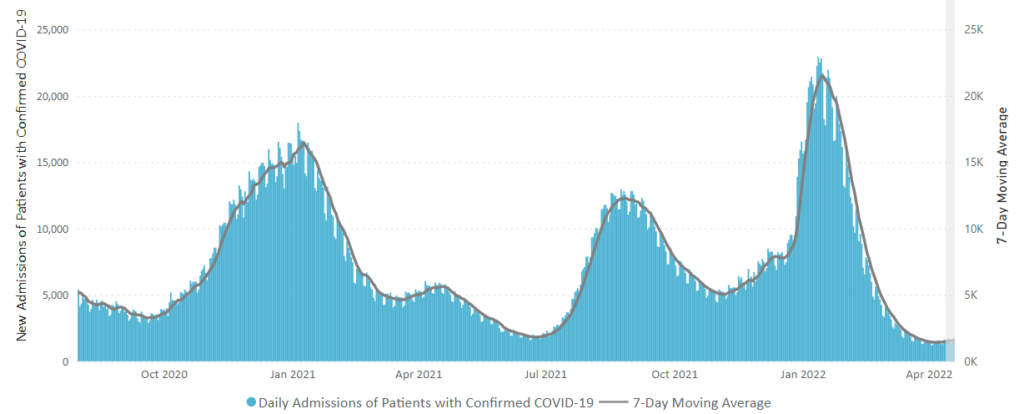
In addition, here’s the CDC’s Chart of Daily Trends in the Number of New COVID-19 Hospital Admissions in the United States:
Can you say endemic?
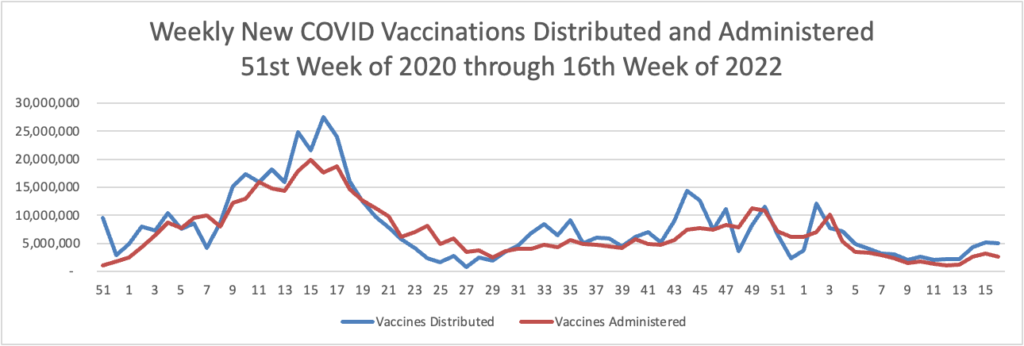
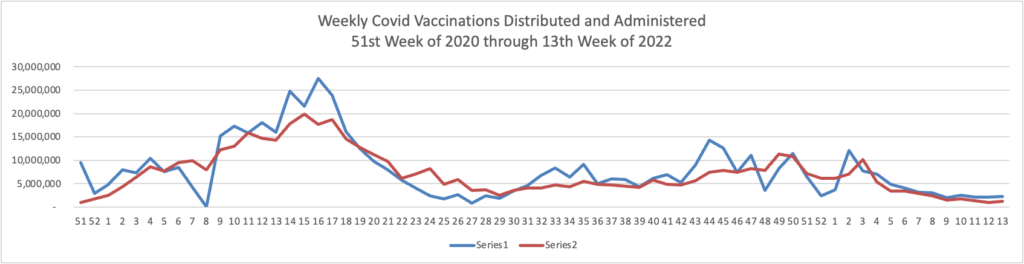
Below you will find the FEHBlog’s weekly chart of Covid vaccinations distributed and administered from the beginning of the Covid vaccination era in December 2020 to the current week 17.
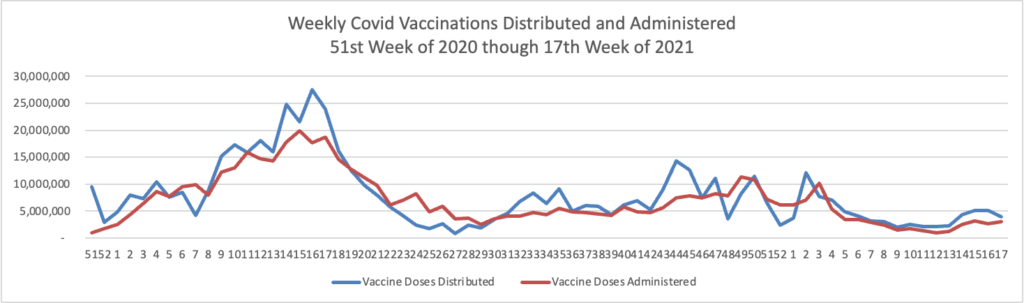
The CDC’s Covid Data Tracker Weekly Review points out, “This week, the U.S. COVID-19 Vaccination Program marks two milestones: 500 days since the first COVID-19 vaccine was approved for use in the United States, and 100 million first booster doses administered.”
In the New York Times, David Leonhardt reports that the FDA is waiting to receive additional data from Pfizer and Modera [likely next month] to support their emergency use authorizations for Covid vaccines for children between six months and five years. Although the FDA’s preference is to give EUAs to both vaccines simultaneously to provide parents a choice, the agency will not delay a EUA decision on one or the other unnecessarily.
The CDC’s weekly review adds,
Currently, there are 54 (1.68%) counties, districts, or territories with a high COVID-19 Community Level, 256 (7.95%) counties with a medium Community Level, and 2,910 (90.37%) counties with a low Community Level. This represents a slight (0.59%) increase in the number of high-level counties, a small (+1.43%) increase in the number of medium-level counties, and a corresponding (−2.02%) decrease in the number of low-level counties. Seventeen (30.36%) of 56 jurisdictions had no high- or medium-level counties this week.
To check your COVID-19 community level, visit COVID Data Tracker.
From the health savings account front, the Society for Human Resource Management reports
Health savings account (HSA) contribution limits for 2023 are going up significantly in response to the recent inflation surge, the IRS announced April 29, giving employers that sponsor high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) plenty of time to prepare for open enrollment season later this year.
The annual inflation-adjusted limit on HSA contributions for self-only coverage will be $3,850, up from $3,650 in 2022. The HSA contribution limit for family coverage will be $7,750, up from $7,300. The adjustments represent approximately a 5.5 percent increase over 2022 contribution limits, whereas these limits rose by about 1.4 percent between 2021 and 2022.
In Revenue Procedure 2022-24, the IRS confirmed HSA contribution limits effective for calendar year 2023, along with minimum deductible and maximum out-of-pocket expenses for the HDHPs with which HSAs are paired.
Here is that 2023 deductible and OOP max information:
For calendar year 2023, a “high deductible health plan” is defined under § 223(c)(2)(A) as a health plan with an annual deductible that is not less than $1,500 for self-only coverage or $3,000 for family coverage [Self-only: +$100 Family: +200 from 2022], and for which the annual out-of-pocket expenses (deductibles, co-payments, and other amounts, but not premiums) do not exceed $7,500 for self-only coverage or $15,000 for family coverage [Self-only: +$450 Family: +$900 from 2022].
From the Medicare Part D front, Fierce Healthcare reports
CMS is giving Part D plans a little extra time to prepare to funnel price concessions to the member at the point of sale.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on Friday finalized a rule with the price concession changes as well as a slew of updates for Medicare Advantage plans.
The agency said in a fact sheet on the regulation that beginning Jan. 1, 2024, it will define the negotiated price for a drug in Part D as the baseline, or lowest possible, payment to a pharmacy to ensure that price concessions are felt at the point of sale by beneficiaries.
“This policy reduces beneficiary out-of-pocket costs and improves price transparency and market competition in the Part D program,” CMS said.
The bell for prescription drug rebates is beginning to toll.
From the healthcare business front, Healthcare Dive tells us
Molina Healthcare in the first quarter recorded its highest COVID-19 costs since the start of the pandemic, CEO Joe Zubretsky said Thursday.
However, those costs were almost entirely offset by members cutting back on healthcare visits, a common trend throughout the pandemic, he said on a call with investors.
After costs peaked in January, they quickly declined in the subsequent months. “When I say [COVID-19 costs] subsided during the quarter, it did so dramatically,” Zubretsky added.
HR Morning discusses a recent Willis Towers Watson survey on how employers are dealing with rising health care costs. To make healthcare more affordable for employees.
Fifty-five percent said their plan is to improve quality and outcomes to lower overall cost. Adding or enhancing low- or no-cost coverage for specific benefits is the plan for 41%. And 32% will be making changes to employees’ out-of-pocket costs, while 21% said they’ll alter their health plan payroll contributions.
From the preventive services front, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force made a final grade D recommendation against initiating low-dose aspirin use for the primary prevention of CVD in adults 60 years or older. “For adults aged 40 to 59 years with an estimated 10% or greater 10-year cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk: The decision to initiate low-dose aspirin use for the primary prevention of CVD in this group should be an individual one.” This is a Grade C recommendation.