Thursday Miscellany
From Capitol Hill, The Hill informs us

A growing number of Senate Democrats say they’re ready to take a tough vote on an amendment to keep the Title 42 health order in place at the U.S.-Mexico border if that’s what’s needed to move a stalled COVID-19 relief package.
Senate Majority Leader Charles Schumer (D-N.Y.) has held the bill from the floor because Republicans are insisting on voting on a bipartisan amendment to overrule the Biden administration’s decision to lift Title 42, a pandemic order that has stopped thousands of immigrants from entering the country on asylum claims. * * *
Without giving in to the Republicans’ demand for a vote on the hot-button issue of securing the border, COVID-19 relief could be stalled until after the November election.
The amendment is expected to fail but it’s a tough vote for vulnerable Senate Democrats.
More likely, in the FEHBlog’s view, the Majority Leader is waiting until the Title 42 health order is lifted later this month to see what happens.
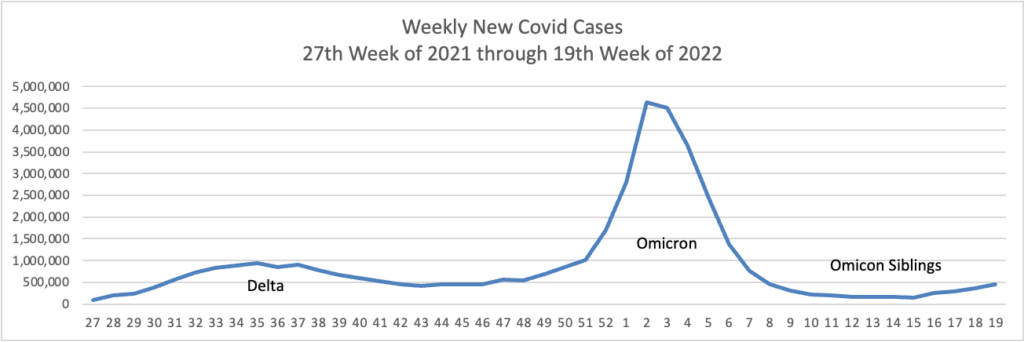
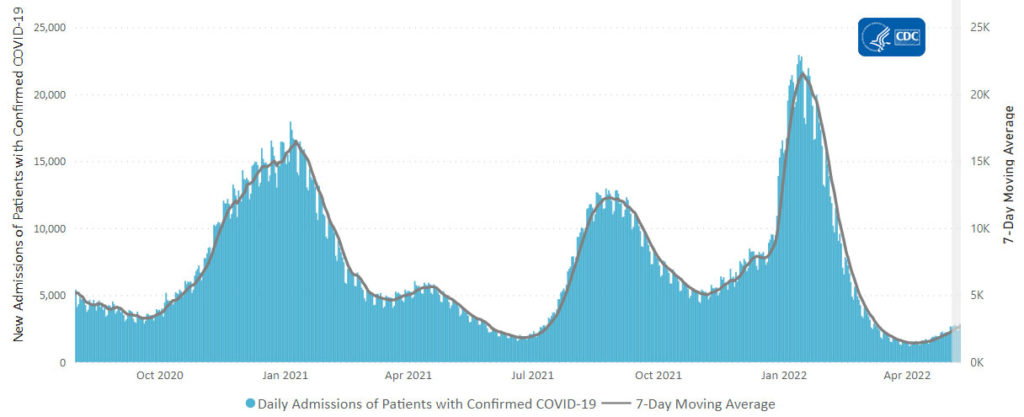
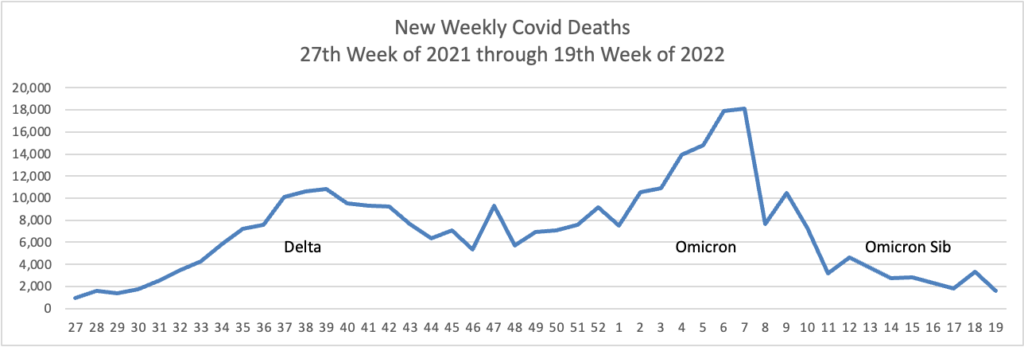
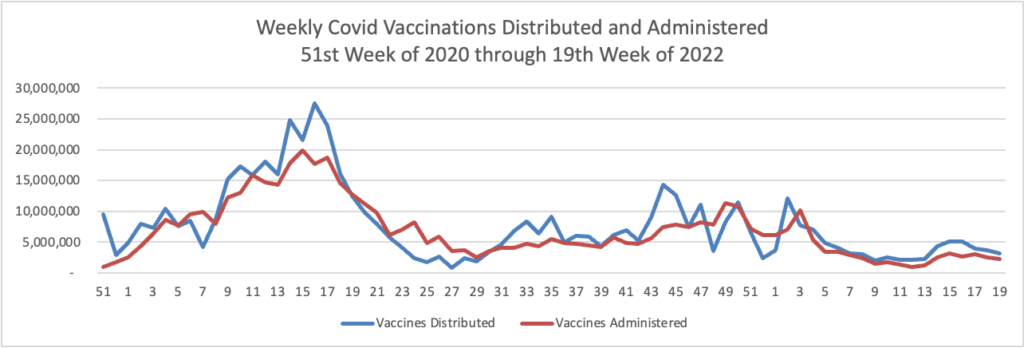
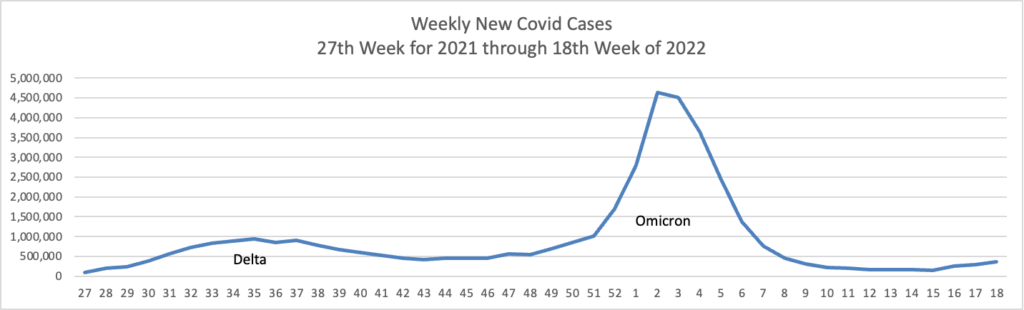
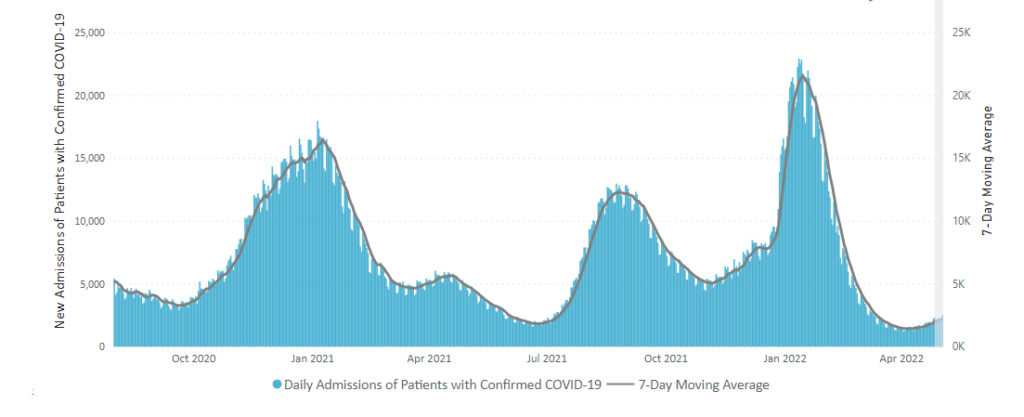
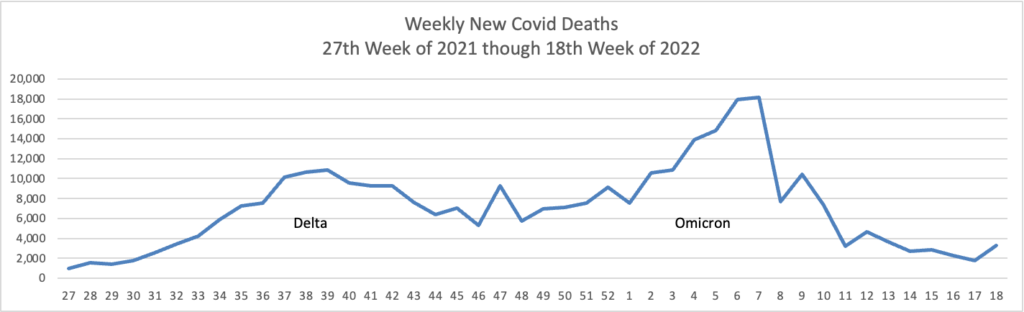
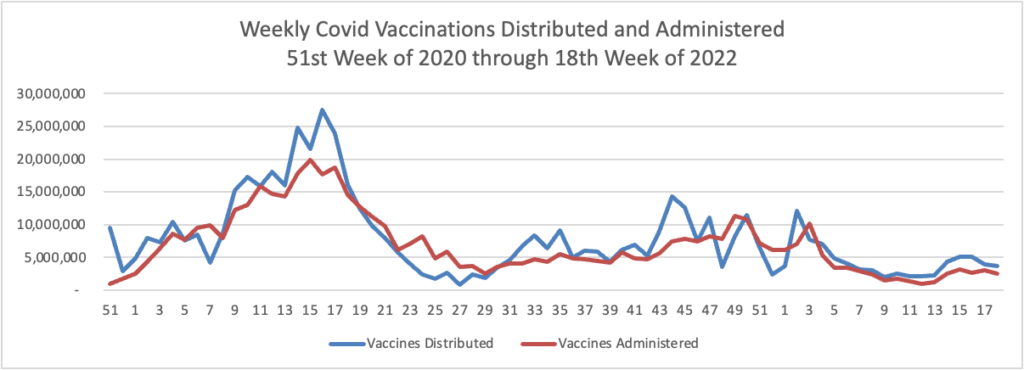
From the Omicron and siblings front —
The Wall Street Journal informs us
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that children ages 5 to 11 receive the newly authorized Covid-19 booster shot from Pfizer Inc. and BioNTech SE.
Following the recommendation Thursday, many of the nation’s doctors, pharmacies and other vaccination sites are expected to begin offering the extra doses to the 28 million U.S. children in the age group.
The shots are to be given five months after the second dose. The extra dose is one-third the amount that those 12 years old and above receive.
Also Thursday, the CDC said it was strengthening its recommendation that people 12 years and older who are immunocompromised, or who are 50 and older, should receive a second booster dose at least four months after their first.
This means that health plans must start covering the booster with no member cost-sharing pursuant to ACA FAQ 50.
The Journal adds
Moderna Inc.’s leader said it is possible the company would be able to start shipping its Covid-19 vaccine for use in young children as soon as early June, pending a decision by U.S. regulators.
“We are ready from a manufacturing standpoint,” Moderna Chief Executive Stéphane Bancel said during a virtual appearance Thursday at The Wall Street Journal’s Future of Everything Festival.
The FDA/CDC decision is expected next month.
In other virus news, STAT News interviewed a top CDC expert on monkeypox. From the FEHBlog’s standpoint, the key takeaway is that monkeypox is not Covid.
I think we can take away a lot from what we know about monkeypox in Congo Basin and in West Africa. Even if human-to-human transmission is documented, it is generally documented among very close contacts. So family members, people taking care of ill patients. Or health care providers.
In funding news, the Department of Health and Human Services announced today a $1.5 billion funding opportunity under the State Opioid Response
SOR grant program provides formula funding to states and territories for increasing access to FDA-approved medications for the treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (OUD), and for supporting prevention, harm reduction, treatment, and recovery support services for OUD and other concurrent substance use disorders (SUD). The SOR program also supports care for stimulant misuse and use disorders, including for cocaine and methamphetamine. The SOR program helps reduce overdose deaths and close the gap in treatment needs across America by giving states and territories flexibility in funding evidence-based practices and supports across different settings to meet local community needs.
From the miscellany department
- Today “the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM) released guidance regarding the implementation of EO 13932; Modernizing and Reforming the Assessment and Hiring of Federal Job Candidates. OPM’s guidance represents a major step towards the federal government’s adoption of skills-based hiring practices and is an important innovation in federal hiring, which has historically relied on education and candidate self-assessments as a proxy for a candidate’s ability to perform in a job. This new approach helps hiring managers recognize and value skills regardless of where they were acquired, whether in a formal degree program, on the job, or on one’s own.”
- Employee Benefit News identifies the ten most popular mental health and wellness apps.
- Benefits consultant Tammy Flanagan discusses federal employee life insurance benefits in Govexec.
- Health Payer Intelligence reports that CMS has updated the Medicare.gov website “to include new features such as highlighting pages that answer popular questions and spotlighting key steps that consumers should take related to Medicare coverage.”