Monday Roundup

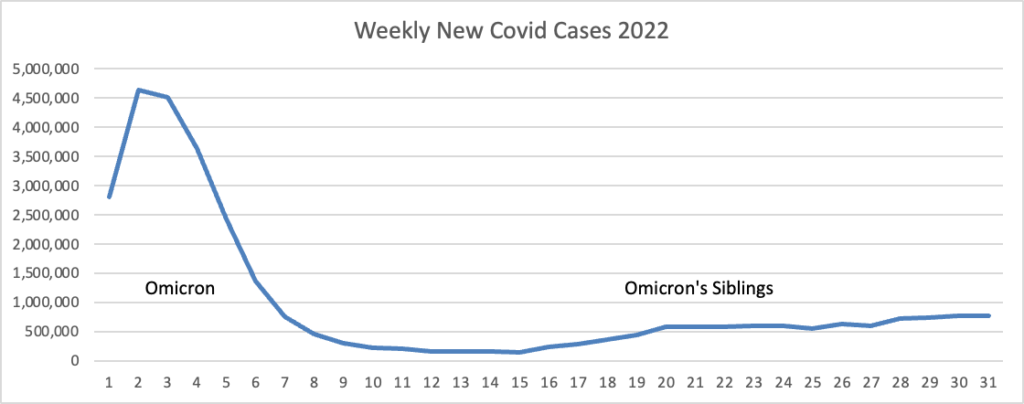
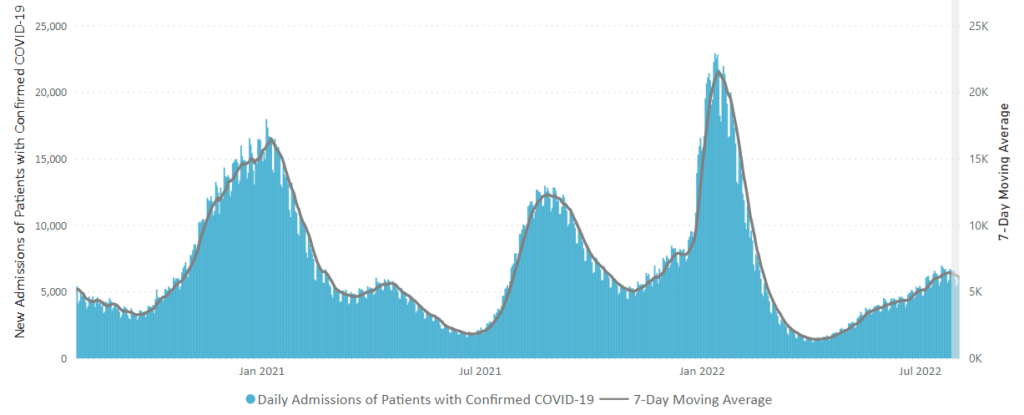
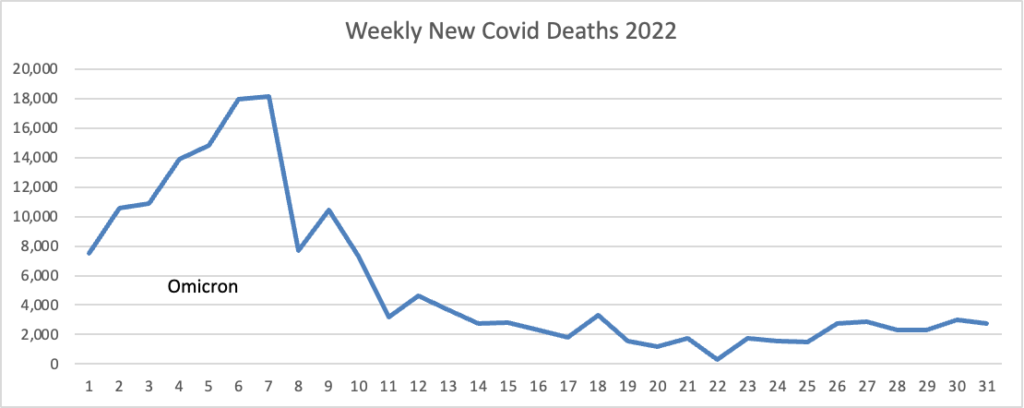
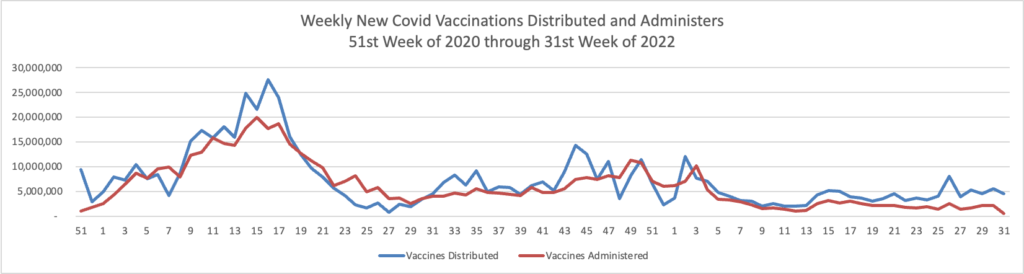
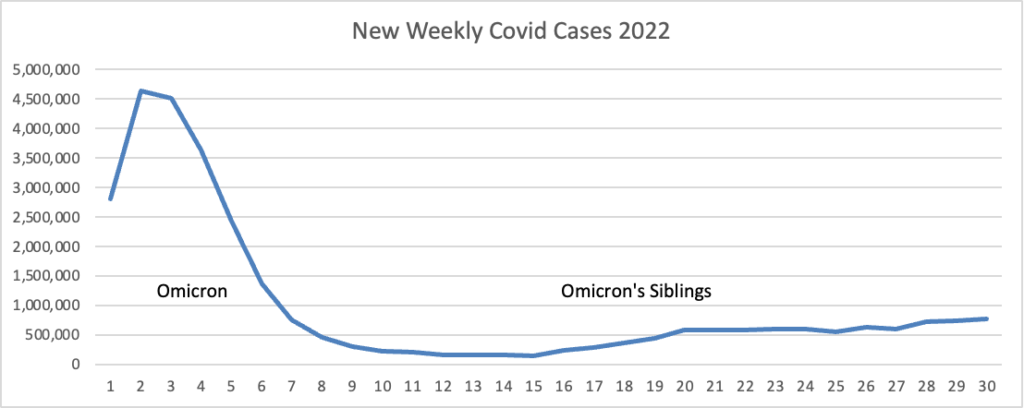
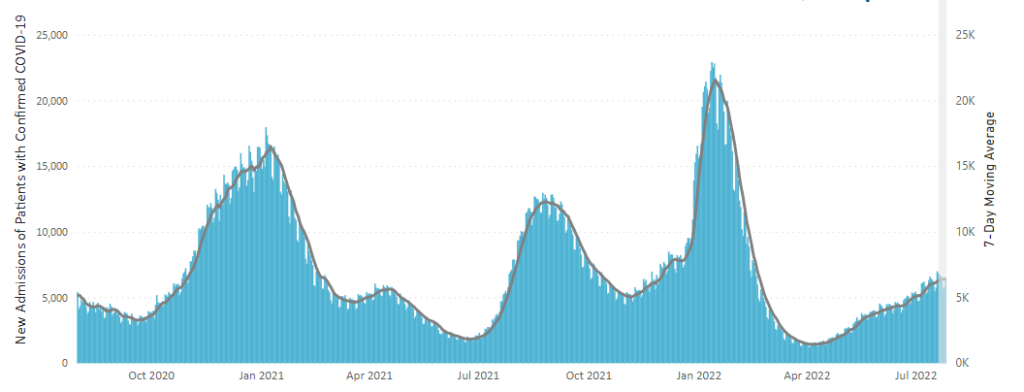
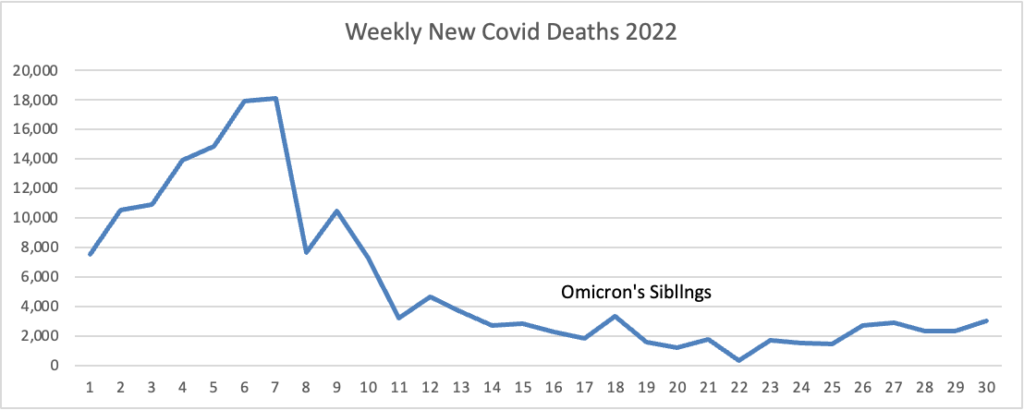
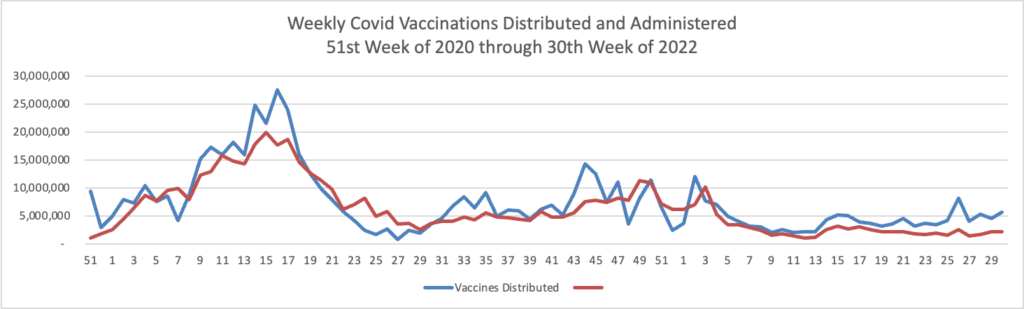
From the Omicron and unusual viruses front —
STAT News reports
Pfizer and BioNTech said Monday that they have asked the Food and Drug Administration to authorize a new booster shot targeted at the Omicron BA.4/BA.5 strain of the coronavirus that causes Covid-19, the first step in a process that could lead to more effective booster shots.
Notably, in the same press release, the companies said that a clinical study investigating the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of the vaccine, which also includes the original Covid strain, is expected to start this month, meaning data would not be available for the FDA to consider.
The application to authorize the vaccine without new clinical trial data is part of a bold and potentially controversial gambit by the U.S. and its advisers to try and get ahead of the fast-mutating coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. But it’s one that could also have a big payoff.
The Pharmacy Times tells us
Officials with the FDA have granted an expanded Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to Novavax for its COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted for adolescents 12 through 17 years of age, according to a press release. The announcement marks the first protein-based COVID-19 vaccine authorized in the United States for this patient population.
The expanded EUA allows for a 2-dose primary series for active immunization to prevent COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 in adolescents. Doses are now available and primary series immunizations for adolescents can begin once the CDC releases a policy recommendation.
Will the next Novovax approval from the FDA be for a booster?
Medpage Today points to a study suggesting a connection between myocarditis in children and long Covid.
The Wall Street Journal adds
Officials in New York are urging pediatricians and parents to bring patients up to date on polio shots, as evidence suggests the infectious and potentially debilitating poliovirus was present in the state as early as April.
Health officials said they have sent alerts to healthcare providers, hung fliers in houses of worship, grocery stores and summer camps, and talked with community leaders to boost polio vaccination rates in the greater New York City area. Some places including Rockland and Orange counties have polio vaccination rates around 60% among eligible children, compared with a national rate of around 93%, according to federal data.
Polio is particularly insidious, health officials and other public-health experts said, because the majority of cases occur in people who never develop symptoms but can still spread the virus. That silent spread can cause meningitis or paralysis in someone unvaccinated against the disease.
In other public health news, STAT News informs us
Anthony Fauci, the top U.S. infectious diseases official for decades and a leading researcher on crises from HIV to Covid-19, announced Monday that he would be stepping down from his positions in December.
Fauci, 81, has led the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases for 38 years, serving a line of presidents from both parties since the Reagan administration. He has also served as President Biden’s chief medical adviser since Biden took office. While Fauci has telegraphed that he was planning on leaving those roles in a matter of months, Monday’s announcement makes it official.
But Fauci, known as a tireless workhorse, said he would not be retiring. “After more than 50 years of government service, I plan to pursue the next phase of my career while I still have so much energy and passion for my field,” he said. “I want to use what I have learned as NIAID Director to continue to advance science and public health and to inspire and mentor the next generation of scientific leaders as they help prepare the world to face future infectious disease threats.”
From the U.S. healthcare business front, Bloomberg reports
Signify Health Inc. soared the most since its shares started trading last year as UnitedHealth Group Inc., Amazon.com Inc., CVS Health Corp. and Option Care Health Inc. competed to acquire the home-health technology and services provider, according to people familiar with the matter.
UnitedHealth has submitted the highest bid in excess of $30 a share, while Amazon’s offer is close behind, the people said, asking not to be identified as the discussions are private. Signify is holding a board meeting Monday to discuss the bids, the people said. * * *
Final bids are expected Sept. 6, but a deal could come earlier if any of the parties preempt the sales process, the people said. * * *
Through its software and services, Signify aims to help clients — payers like health plans, government programs and employers — shift to value-based payment plans. It’s backed by private equity firm New Mountain Capital, which formed the company in 2017, according to the firm’s website.
That is quite a big business rumble.
From the No Surprises Act front, Prof. Katie Keith and her colleagues wrote two articles on last Friday’s “final, final” independent dispute resolution rule — one concerns its impact on IDR arbitrations and the other on miscellaneous topics.
From the mental healthcare front, Health Payer Intelligence lets us know that “Payers are working toward achieving broader access to mental healthcare and behavioral healthcare services by reimbursing at higher rates and supporting primary care” according to a recent AHIP survey.
Nearly eight in ten health plans had boosted behavioral healthcare workers’ reimbursement rates (78 percent). Additionally, 83 percent of payers had attracted and retained a diverse population of behavioral healthcare providers.
Substance abuse care is becoming more accessible, the survey found. Specifically, more providers have become eligible to offer medication-assisted therapy (MAT). This population has expended 114 percent over the course of three years.
Nearly three-quarters of health plans (72 percent) support behavioral healthcare training for primary care providers. The same share supported primary care providers by helping them find behavioral healthcare specialist referral partners.
Payers have also offered primary care providers the opportunity to call behavioral healthcare specialists via telehealth or telephone in order to consult them on a patient’s condition. More than half of the health plans (56 percent) provide this option. This method has been used in pediatric psychiatry to solve members’ challenges in connecting with specialists.
Health plans reported a couple of main ways that they try to connect members with mental healthcare services. Many plans do this by supporting patient navigation (83 percent). For example, health plans might connect members with community-based organizations that can address their social determinants of health needs.
Additionally, more than eight in ten health plans said they help members secure behavioral healthcare visits. Follow-up on inpatient care and emergency room visits is often part of health plans’ efforts to connect members with mental health services as well. Seventy-eight percent of the plans leveraged specialized case managers to perform this function.
From the medical research and development front —
Biopharma Dive informs us
Gilead’s long-acting HIV shot Sunlenca is now cleared for sale in Europe, marking the first marketing authorization for a treatment the California biotechnology company hopes can be used broadly as a standard therapy and preventive regimen.
The decision by the European Commission, announced Monday, authorizes Sunlenca for patients whose current treatment regimen can no longer keep their infection at bay. Sunlenca, previously called lenacapavir, will be added to other antiviral drugs to boost patients’ immune response and reduce levels of virus in the body.
Gilead is still waiting on a regulatory decision in the U.S., where it has been delayed by manufacturing issues. An approval by the Food and Drug Administration’s December deadline could put the drug on track to reach sales that RBC Capital Markets analysts estimate will climb as high as $4 billion a year.
The Wall Street Journal reports
Zapping the brain with weak electrical currents that mimic normal neural activity can boost memory in healthy older adults, at least over the short term, researchers said in a study published Monday in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Electrical stimulation of the brain as a potential tool for enhancing memory is a growing field of research, with experiments showing that the ability to recall memories depends upon synchronized activity between different brain regions.
The new research, conducted on people over age 65, “adds to the growing evidence that noninvasive stimulation mimicking the rhythmic brain activity that supports cognition can improve memory” in this population, said Joel Voss, a University of Chicago professor of neurology who wasn’t involved in the research.