Thursday Miscellany

From Capitol Hill, the American Hospital Association tells us
The Senate today passed (68-29) an amended version of the $1.7 trillion omnibus appropriations bill that funds the federal government through the end of the current fiscal year. The legislation also includes many provisions affecting hospitals and health systems.
The Senate also passed another short-term continuing resolution through Dec. 30 to allow time for the more than 4,000-page legislation to be enrolled and for President Biden to sign it. This ensures there will be no interruption of services or federal shutdown.
The omnibus spending bill, which includes relief from Medicare cuts and extensions of rural and telehealth programs, as well as the Dec. 30 continuing resolution, now go to the House, which is expected to consider them today . The president is expected to sign the short-term continuing resolution before current funding for the government expires at 11:59 p.m. ET on Dec. 23, and to sign the omnibus later next week.
The Wall Street Journal adds, “House Majority Leader Steny Hoyer (D., Md.) said the House would vote on the bill Friday.”
In other 2023 Consolidated Appropriations Act or omnibus news
- The Hill reports on “last minute” changes to the omnibus, including provisions assisting nursing and pregnant workers.
- Mercer Consulting alerts us to a two-year-long extension of telehealth flexibilities available to high deductible plans with health savings accounts.
- Think Advisor and the Wall Street Journal provide an overview of the Secure 2.0 Act provisions in the omnibus. The Secure 2.0 Act affects 401(k) plans offered to employees and IRAs. The key provision that takes effect for 2023 is an increase in the required minimum distribution age from 72 to 73.
- The Wall Street Journal reviews the other omnibus provisions affecting businesses.
From the public health front —
Beckers Hospital Review informs us
While the respiratory “tripledemic” continues to slam emergency rooms and children’s hospitals, there are two glimmers of hope on the horizon, according to a Dec. 22 report in The New York Times.
COVID-19, the flu and respiratory syncytial virus attack the body in different ways, and there are varying levels of disease severity across the U.S. Today, some scientists say RSV has peaked in most parts of the country.
“I think it’s likely that the RSV season has peaked in most parts of the country,” said Virginia Pitzer, ScD, an infectious disease epidemiologist at New Haven, Conn.-based Yale School of Public Health. “I think that there is a light at the end of the tunnel.”
Additionally, there’s reason to believe next winter won’t be as burdensome for the American population and healthcare organizations.
Ironically, the safety precautions used to help stem the pandemic in the past couple of years have also kept adults and children from being exposed to the viruses that typically circulate this time of year, said Dr. Pitzer.
“There was a bit of a buildup of susceptibility at the population level,” she added. “It’s a worse than normal winter, but one that hopefully will not be repeated next year.”STS
The American Hospital Association tells us
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America today recommended hospitals and health systems no longer routinely screen symptom-free patients for COVID-19 upon admission or before procedures and rely instead on enhanced layers of infection prevention interventions.
“The small benefits that could come from asymptomatic testing at this stage in the pandemic are overridden by potential harms from delays in procedures, delays in patient transfers, and strains on laboratory capacity and personnel,” said Thomas R. Talbot, M.D., MPH, the chief hospital epidemiologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, and a member of the SHEA Board of Directors. “Since some tests can detect residual virus for a long period, patients who test positive may not be contagious.”
STAT News reports
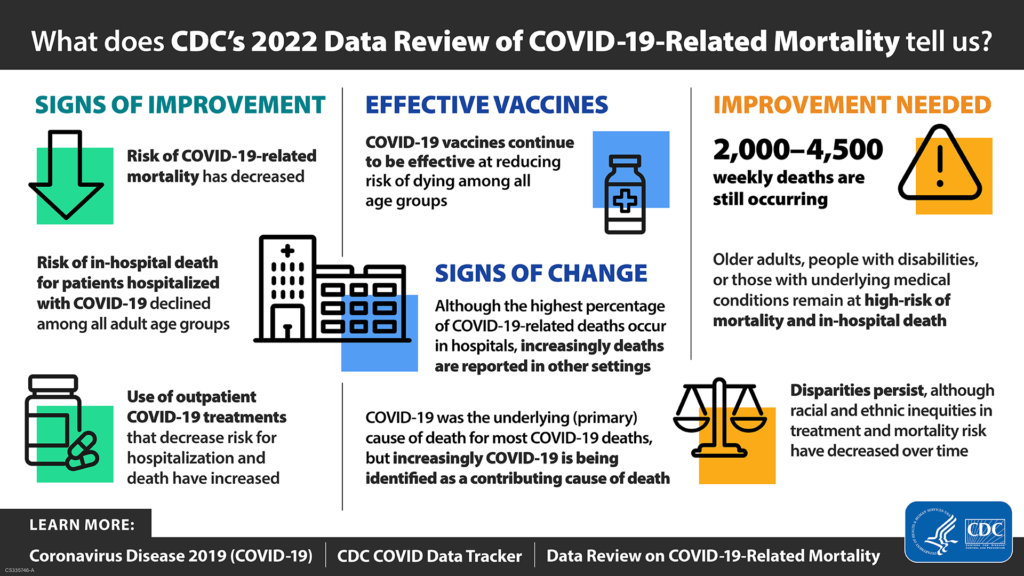
[According to a CDC report, a] baby born in the U.S. in 2021 has a life expectancy of 76.4 years, down from 77 years in 2020 and the lowest level the CDC has recorded since 1996. The age-adjusted death rate for Covid rose by 22.5% between 2020 and 2021, while death rates from unintentional injuries — one-third of which come from overdoses — rose by 12.3%.
HHS’s Agency for Healthcare Quality and Researched refreshed its Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Fast Stats website. The site provides “summary statistics on inpatient stays, emergency department visits, and priority topics, by select characteristics.”
From the OPM front, OPM’s medical director, Dr. Ron Kline announced today on Linked In that he is leaving OPM to take a new position beginning January 17, 2023 as
the Chief Medical Officer of the Quality Measurement and Value-Based Incentives Group (QMVIG) at the Center for Clinical Standards and Quality (CCSQ) at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
QMVIG is responsible for developing, evaluating and supporting the implementation of quality measurement programs across the entire federally-supported health care continuum. This includes Medicare’s Quality Payment Program and the Inpatient (i.e. Hospital) Quality Reporting Program. These measures and policies guide these innovative programs to improve healthcare quality for all Americans.
Best wishes, Dr. Kline, and thanks for your work with the FEHB over the past 3 1/2 years.
From the Rx coverage and medical research fronts –
MPR reports
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Actemra (tocilizumab) for intravenous (IV) use to treat COVID-19 in hospitalized adults who are receiving systemic corticosteroids and require supplemental oxygen, noninvasive or invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
ICER released evidence reports on Alzheimer’s Disease treatments (draft) and hemophilia A and B (final) STAT News explains
The latest Alzheimer’s disease treatment from Eisai and Biogen needs to be cheaper than $20,000 a year to be cost-effective, according to a draft analysis from an influential nonprofit organization published Thursday.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, or ICER, dug into the evidence for lecanemab and concluded that the drug’s demonstrated benefits, a modest but statistically significant delay in the advance of Alzheimer’s, are worth between $8,500 and $20,600 per year. ICER’s calculations, which could change in response to public comment over the next month, are based on metrics meant to quantify the value of improvements to quality of life.
Eisai, which is leading the effort to commercialize lecanemab, has not disclosed how much it will charge for the medicine, saying only that it will prize affordability and access. That will soon change, as the drug, a twice-monthly infusion, is expected to win a preliminary Food and Drug Administration approval by Jan. 6. * * *
Lecanemab’s safety has come into sharp focus over the past two months after three patients died of major brain bleeds.
Regarding hemophilia therapies, ICER observes
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) today released a Final Evidence Report assessing the comparative clinical effectiveness and value of etranacogene dezaparvovec (Hemgenix, CSL Behring,) for hemophilia B. ICER also updated the previous Hemophilia A assessment on valoctocogene roxaparvovec (Roctavian™, BioMarin).
Key recommendations stemming from the roundtable discussion include:
- The value of high-impact single and short-term therapies should not be determined exclusively by estimates of long-term cost offsets, particularly when the existing standard of care is acknowledged to be priced significantly higher than reasonable cost-effective levels.
- Payers should work with manufacturers to develop and implement outcomes-based agreements to address the uncertainty and the high cost of gene therapies for hemophilia.
- At least one national payer has suggested to patient representatives that step therapy with emicizumab is being considered prior to provision of coverage for Roctavian. Clinical experts and patient experts view this approach as lacking any clinical justification and appears to be only a method for trying to avoid the high one-time fee for gene therapy while assuming that patients may switch insurers before the cost-saving potential of gene therapy is fully realized. In short, step therapy does not appear to be a reasonable consideration for this treatment.
ICER’s detailed set of policy recommendations, including comprehensive considerations for establishing evidence-based prior authorization criteria, is available in the Final Evidence Report and in the standalone Policy Recommendations document.
NIH announced
Scientists used patient stem cells and 3D bioprinting to produce eye tissue that will advance understanding of the mechanisms of blinding diseases. The research team from the National Eye Institute (NEI), part of the National Institutes of Health, printed a combination of cells that form the outer blood-retina barrier—eye tissue that supports the retina’s light-sensing photoreceptors. The technique provides a theoretically unlimited supply of patient-derived tissue to study degenerative retinal diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Amazing.
From the miscellany department, the Wall Street Journal and MedPage Today explore the new AI text tool known as ChatGPT. From the Journal article
If you haven’t yet tried ChatGPT, OpenAI’s new artificial-intelligence chatbot, it will blow your mind. Tell the bot to write you anything—an email apologizing to your boss, an article about the world’s richest hamster, a “Seinfeld” script set in 2022—and it spits out text you’d think was written by a human. Knowledge of the topic, proper punctuation, varied sentence structure, clear organization. It’s all there.