
Following up on this week’s posts
Forbes unpacks the colonoscopy study that the FEHBlog discussed in Monday’s post. The critical consideration is that “while colonoscopy may not be the gold standard it’s been made out to be, one or more colorectal cancer screening tools are essential to detect cancer and lower mortality rates.” Check it out.
Prof. Katie Keith writing in Health Affairs Forefront explores the final family glitch rule that the FEHBP mentioned in yesterday’s post. Two points suggest to the FEHBlog that the final rule will not materially impact the FEHB Program.
This situation—where employee-only coverage is affordable, but family coverage is not—is not uncommon. Most employers offer family coverage, but many do not subsidize it for family members which keeps the cost high for workers and their families.
That’s not the case in the FEHB Program. Moreover,
The final rule will not affect liability under the employer mandate, a fact confirmed by the IRS. Why not? The employer mandate requires certain large employers to offer coverage to employees and dependents. But penalties for violating the mandate are triggered only when an employee receives premium tax credits through the marketplace. The final rule extends premium tax credits to only the family members of workers who are not offered affordable job-based family coverage. It does not affect the eligibility of employees and thus does not implicate the employer mandate.
That’s an important consideration. Implementing the final rule is OPM’s responsibility as the FEHB Program’s regulator.
From the Omicron and siblings’ front —
The Associated Press reports
The White House on Tuesday said eligible Americans should get the updated COVID-19 boosters by Halloween to have maximum protection against the coronavirus by Thanksgiving and the holidays, as it warned of a “challenging” virus season ahead.
Dr. Ashish Jha, the White House COVID-19 coordinator, said the U.S. has the tools, both from vaccines and treatments, to largely eliminate serious illness and death from the virus, but stressed that’s only the case if people do their part. * * *
So far the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only about 11.5 million Americans have received the updated shots, which are meant to provide a boost of protection against both the original strain of COVID-19 and the BA.5 variant that is dominant around the world. Jha said studies suggest that if more Americans get the updated vaccines, “we could save hundreds of lives each day this winter.”
The American Hospital Association informs us
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention today recommended Moderna’s bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster for children aged 6-17 and Pfizer’s bivalent COVID-19 vaccine booster for children aged 5-11 after the Food and Drug Administration authorized them for these ages. CDC previously recommended the Pfizer bivalent booster for Americans 12 and older and the Moderna bivalent booster for adults. The boosters protect against the most recently circulating omicron variants as well as the original virus strain.
MedPage Today offers more information on this FDA decision and a modeling study of 1.2 million global Covid patients showing (1) “Long COVID — defined as one or more clusters of symptoms lasting three months or longer — occurred in about 6% of people with symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection” and (2) “at one year, 15% of long COVID patients had ongoing cognitive or respiratory problems or fatigue.”
In other public health news, NPR offers a transcript of a monkeypox discussion among NPR healthcare reports. The upshot is
Just a few months ago, it looked like the U.S. had lost its chance to get monkeypox under control. Cases were soaring, and vaccines were in short supply. But now the story has taken a turn and this time in a good direction. In fact, some disease experts are even raising the idea that the U.S. could nearly eliminate the virus.
From the medical research front —
Healthcare Dive reports
Walmart is getting into clinical trials with the launch of the Walmart Healthcare Research Institute, as the retail giant focuses on high-margin businesses in healthcare.
Walmart said the venture is meant to improve diversity in clinical trials, focusing on interventions and medications that can make an impact in underrepresented communities. That includes older adults, rural residents, women and minority populations, the company said in a release.
It could also become a valuable stream of revenue for Walmart from drug companies looking for participants for potential trials and studies.
The NIH Directors’ Blog tells us about two NIH-supported chemists, Carolyn R. Bertozzi and K. Barry Sharpless, who won the 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work in click chemistry.
This form of chemistry has made it possible for researchers to snap together, like LEGO pieces, molecular building blocks to form hybrid biomolecules, often with easy-to-track imaging agents attached. Not only has click chemistry expanded our ability to explore the molecular underpinnings of a wide range of biological processes, but it has provided us with new tools for developing drugs, diagnostics, and a wide array of “smart” materials.
Kudos to the winners.
STAT News reports
Merck on Wednesday agreed to extend an ongoing collaboration with Moderna to develop a personalized vaccine for the treatment of patients with skin cancer.
Moderna is getting $250 million from Merck to secure opt-in rights to the cancer vaccine candidate, called mRNA-4157. The two companies are jointly conducting a mid-stage clinical trial that combines the customized, mRNA-based vaccine with Merck’s checkpoint inhibitor Keytruda.
Results from this randomized study will be announced before the end of the year, but the timing of Wednesday’s deal suggests Merck and Moderna have seen enough encouraging data to advance mRNA-4157 into larger studies.
From the Rx coverage front, the HHS Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality updated its consumer tool “How To Create a My Medicines List,” previously known as “My Pills List.”
From the healthcare quality front, NCQA released a slide deck and recording of last week’s Future of HEDIS webinar focused on health equity.
From the maternity care front, Health Day reports on a March of Dimes report on maternity care deserts and related matters. Here’s the federal government’s maternity care map:
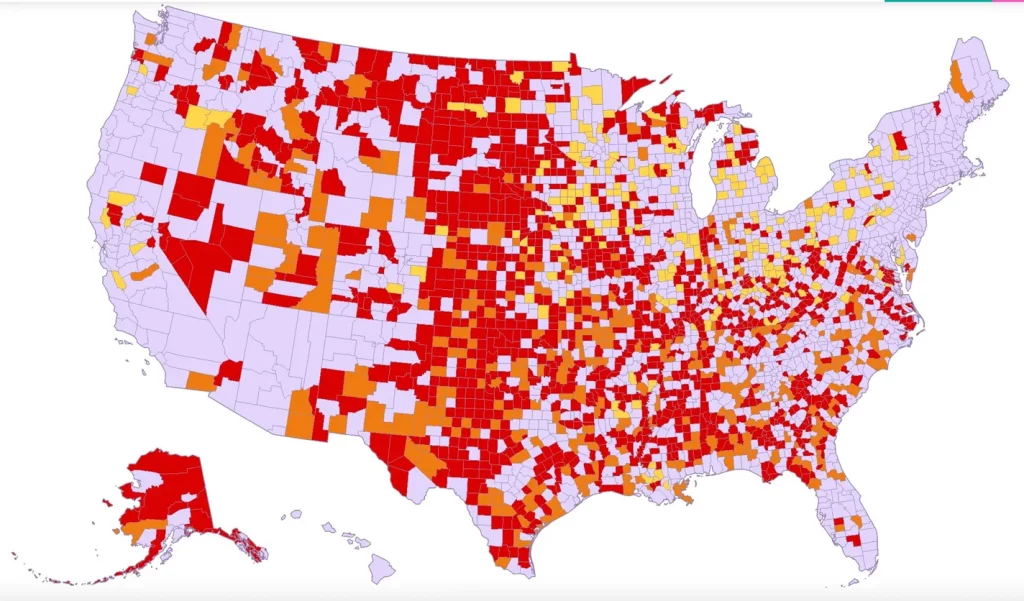
Maternity care deserts [red]: low access [orange]; moderate access [yellow]; full access [light purple] Source: U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), Area Health Resources Files, 2021
