Based on the Centers for Disease Control’s Covid Data Tracker and using Thursday as the first day of the week, here is the FEHBlog’s updated weekly chart of new Covid cases:
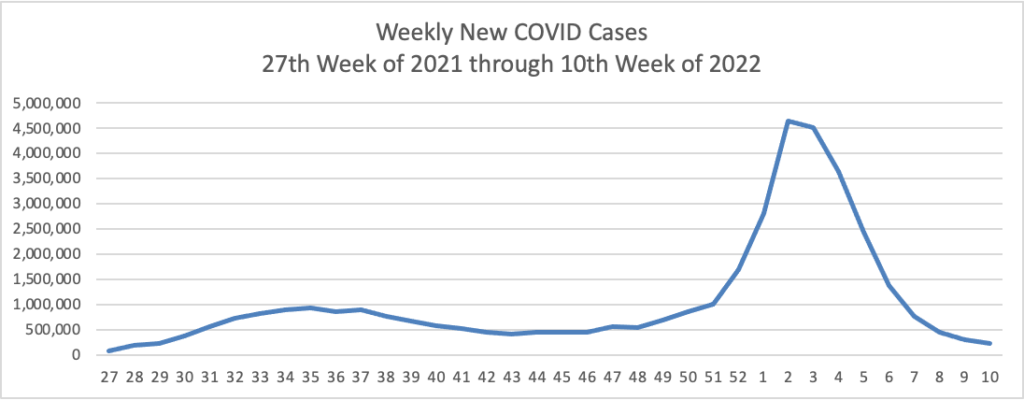
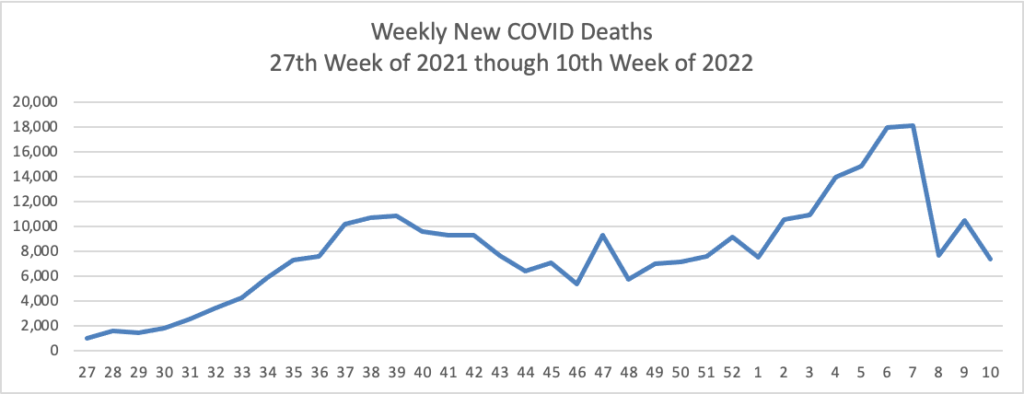
Not quite as low as we were in early July but very much moving in the right direction. So is the FEHBlog’s updated weekly chart of new Covid deaths, which is considered a lagging indicator.
The epidemiologists have a keen eye out for new worrisome variants. For example, for other troubling variants, Becker’s Hospital News tells us about a relatively new combination of Delta and Omicron known as Deltacron.
The recombinant variant appears unlikely to spread as easily as delta or omicron, William Lee, PhD, vice president of science at Helix, told USA Today. “We have not seen any change in the epidemiology with this recombinant,” WHO COVID-19 technical lead Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, said of deltacron during a March 9 media briefing. “We haven’t seen any change in severity. But there are many studies that are underway.”
Here’s the FEHBlog’s weekly chart of Covid vaccinations distributed and administered from the start of the Covid vaccination era in late 2020 until the week ended this past Wednesday.
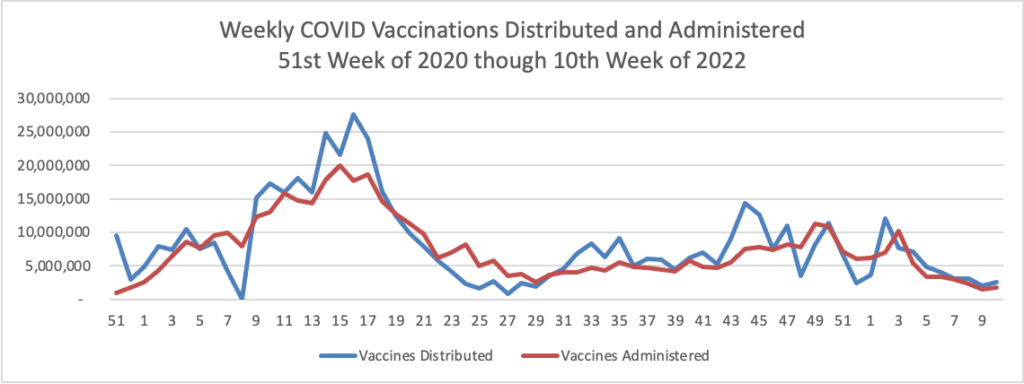
It is noteworthy that this week, the percentage of Americans aged 18 and older who are fully vaccinated (two doses of mRNA vaccine) cracked 75%. The same cadre is closing in on being 50% boostered. The most at risk, over age 65 cadre is 89% fully vaccinated and 66.7% boostered.
The American Hospital Association adds
In a study of 1,364 children aged 5-15, two doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of omicron infection by 31% in those under 12 and 59% in older children, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported today. CDC said the study reinforces the importance of vaccination to keep children and teens protected from severe disease, noting that another recent study found the vaccine 92%-94% effective against COVID-19 hospitalization in adolescents during the delta surge and 74% effective against hospitalization in younger children during omicron.
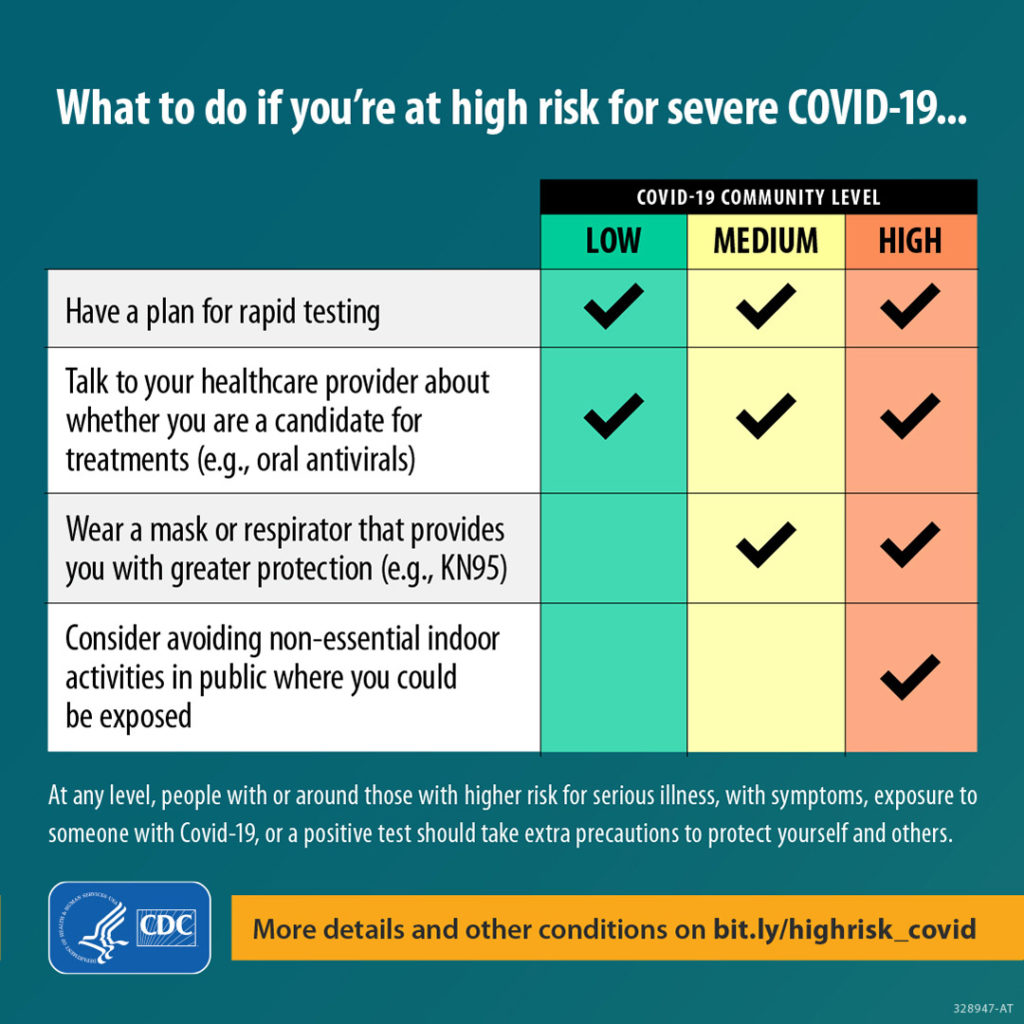
Here’s a link to the CDC’s weekly review of its Covid statistics. This week’s issue focuses on protecting folks at high risk for Covid, such as the immunocompromised.
Who is most likely to become very sick or die from COVID-19? Your chances increase with age and underlying medical conditions like cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, dementia, and obesity, particularly if you’re not up to date on vaccinations. People with weakened immune systems,* some disabilities, some mental health conditions, and some chronic diseases are also at higher risk. A lot of people might not know they’re at risk for severe illness—review the list to find out if you could be.
Here’s a link to the CDC’s weekly Fluview report, which states that flu activity is increasing in “most of the country.” In this regard, the American Medical Association inform us
Healio (3/10, Downey, Gallagher) reports “interim estimates published Thursday in” the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report “indicate that this season’s influenza vaccine has not been effective.” Based on the data “from more than 3,600 children and adults,” researchers “estimated that the vaccine has been 16% effective against mild or moderate influenza caused by the predominant circulating virus, influenza A(H3N2), with a 95% confidence interval…that suggests vaccination ‘did not significantly reduce the risk of outpatient medically attended illness’ caused by H3N2.”
From Capitol Hill and closing the loop on Thursday’s post, the Senate did pass the fiscal year 2022 omnibus appropriations act Thursday night. Roll Call reports
On a 68-31 vote, the Senate passed the 2,700-page, $1.5 trillion omnibus containing all 12 fiscal 2022 spending bills, $13.6 billion in supplemental appropriations to address the crisis in Ukraine and a lengthy list of unrelated measures fortunate enough to ride on the must-pass vehicle.
From the No Surprises Act front, the FEHBlog had been concerned that the federal regulators were giving up on using the Qualified Payment Amount as a rebuttable presumption in NSA arbitrations which would help tremendously to control out of network benefit and plan legal costs. The FEHBlog therefore was encouraged to find that the federal government has filed a brief with the federal district court for the District of Columbia defending that position in a case raising the same issue. An oral argument on this issue will be heard by District Judge Richard Leon on March 21, 2022, at 3 pm. The FEHBlog will keep an eye on this and the other federal cases raising this issue.
From the electronic health record front, MedCity News interviews the CEO of Epic Systems at the Vive conference. The interview covers interoperability, artificial intelligence and other timely topics.
From the opioid epidemic front, STAT News reports
It was in the mid-2010s, the researchers heard, when “tranq dope” — opioids that contained the veterinary tranquilizer xylazine — took off in Philadelphia. But now, in some places across the U.S., it was appearing in 1 in 5 overdose deaths. A recent study also found the powerful synthetic opioid fentanyl in nearly every xylazine-involved death as well, indicating it wasn’t just the tranquilizer causing these overdoses. Experts are still trying to understand the risks of xylazine, but they’re worried because the drug is not an opioid but acts as a sedative, which can increase the risk of a fatal overdose. It might also make it harder to reverse those overdoses with naloxone, which is designed to work on opioids. STAT’s Andrew Joseph has more on how adulterated — and in turn, increasingly dangerous — the U.S. drug supply has become.
Rur roh.
